| Journal of Neurology Research, ISSN 1923-2845 print, 1923-2853 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Neurol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.neurores.org |
Case Report
Volume 4, Number 1, February 2014, pages 41-48
Is Regression of Intracranial Germinoma Spontaneous or DiagnosticRadiation-Induced? A Case Report
Yuichiro Yoneokaa, b, Naoto Watanabea, Masayasu Okadaa, Kazuhiro Andoa, Yukihiko Fujiia
aDepartment of Neurosurgery, Brain Research Institute, University of Niigata, Japan
bCorresponding author: Yuichiro Yoneoka, Department of Neurosurgery, Brain Research Institute, University of Niigata, Japan
Manuscript accepted for publication February 5, 2014
Short title: Regression of Intracranial Germinoma
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jnr264w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Although several case reports describing about “spontaneous” regression of primary intracranial germinoma are available, intensive analysis of those reports suggests diagnostic radiation as a possible cause of the regression in those reports. We present a case of regression of intracranial germinoma, which advocates diagnostic radiation as a cause of previously reported regression of intracranial germinoma. A 22-year-old female student was forced to repeat a grade in school due to unusual fatigue. Despite 4-year absence of her menstrual period as a woman of reproductive age, she did not receive medical attention until experiencing unusual fatigue with visual disturbance and undermined learning. Initial endocrinological work-up revealed panhypopituitarism with masked diabetes insipidus. Magnetic resonance imaging showed a suprasellar tumor, involving the neurohypophysis, optic chiasm and hypothalamus, with spinal dissemination. Endoscopic transnasal biopsy provided pathological confirmation of germinoma, which was treated with craniospinal irradiation. Regression of the suprasellar lesion after cranial computed tomography during radiation therapy planning was demonstrated on serial magnetic resonance imaging. The patient obtained remission and regained a nearly normal level of activity under hormone replacement therapy, but restriction of her visual fields did not improve sufficiently. Diagnostic radiation can induce the regression of intracranial germinoma. Clinicians should keep this diagnostic radiation-induced regression of germinoma in mind and should eliminate unnecessary irradiation to germinoma throughout the diagnostic process. Inadvertent diagnostic radiation can hide fine lesions to be treated.
Keywords: Primary intracranial germinoma; Spontaneous regression; Diagnostic radiation; Diagnostic radiation-induced regression
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Spontaneous regression and remission from cancer was defined by Cole and Eversion in 1956 [1]. Examples of the spontaneous regression of primary intracranial germinomas can be found in the literature from authoritative journals [2-6].
We previously reported a case of synchronized multiple regression of primary intracranial germinoma [7]. In that report, we suggest the synchronized multiple regression as a diagnostic radiation-induced regression (DRIR).
Here, in this report, we present a case of regression of disseminated primary intracranial germinoma, which advocates diagnostic radiation as a cause of previously reported regression of intracranial germinoma on serial magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. We discuss whether these regressions are spontaneous or diagnostic radiation-induced and try to establish a new clinical entity of DRIR.
Clinicians, in particular, among the neurological field should keep this DRIR of germinoma in mind and should eliminate unnecessary irradiation to germinoma throughout the diagnostic process. Inadvertent diagnostic radiation can hide fine lesions to be treated.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 22-year-old female student was forced to repeat a grade in school due to unusual fatigue. She was delivered by Caesarean section with birth weight of 2,700 g. She experienced menarche at 14 years old. Her menstrual cycle had been irregular from the menarche until amenorrhea occurred. She had been well until the summer when she was 18 years old, a first year college student. She had been noticing the fatigue since the summer and also realized her tendency to feel excessive thirst and to drink a significant amount of water at that time of onset. Although the polydipsia associated with polyuria gradually decreased in the next several months, general malaise with amenorrhea occurred around the same time as well as accompanying weight loss. She believed these series of symptoms to be summer lethargy (“natsu-bate” in Japanese) and did not seek medical attention. Despite general malaise with amenorrhea, she patiently attended college until experiencing unusual fatigue with visual disturbance undermined learning when she turned 22 years old. Visual field test revealed her not-so-symmetric bitemporal hemianopsia (Fig. 1). Initial endocrinological work-up revealed hypopituitarism with masked diabetes insipidus (DI) and hyperprolactinemia (Table 1). Cerebrospinal fluid levels of beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and placental-like alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) were elevated (Table 2). MR imaging showed a suprasellar tumor, involving the neurohypophysis, optic chiasm, hypothalamus, corpus callosum and basal ganglia (Fig. 1), with a spinal lesion (Fig. 2A, B).
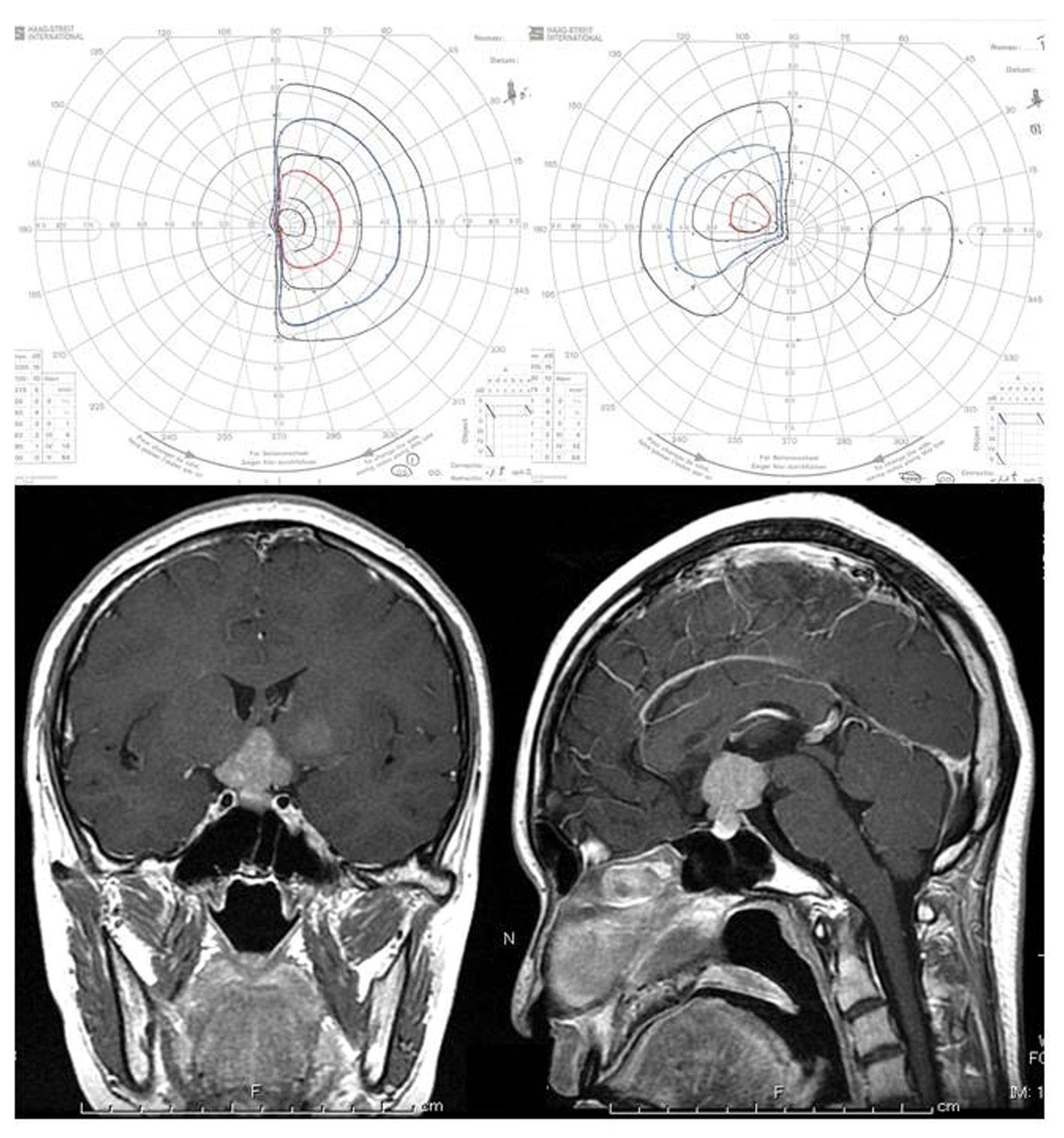 Click for large image | Figure 1. Upper: Goldmann perimeter reveals asymmetric bitemporal hemianopsia. Lower: Post-contrast MR imaging showed a contrast-enhanced sellar-suprasellar tumor and a light-enhanced lesion in the left basal ganglia. |
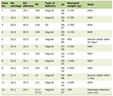 Click to view | Table 1. Laboratory Data on Admission |
 Click to view | Table 2. Tumor Markers |
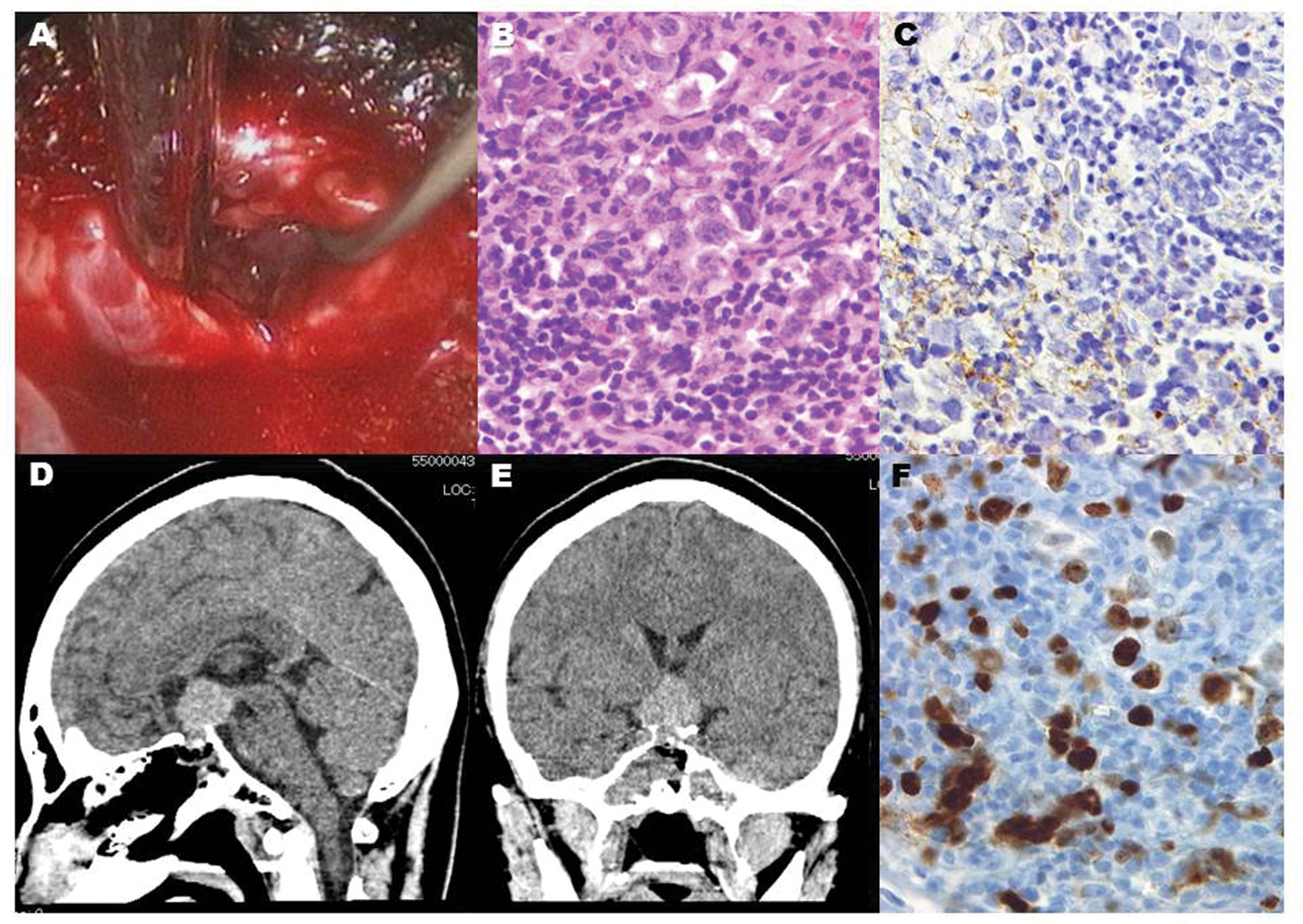 Click for large image | Figure 2. Endoscopic vision revealed grayish gelatinous tissue behind the thinned adenohypophysis (A). Histological diagnosis showed a biphasic population of mature lymphocytes and larger germinoma cells (B), staining of the cytoplasm and cytoplasmic membrane with placental alkaline phosphatase (C), and many MIB-1 positive cells (F), which are compatible with pure germinoma. Post-operative CT scans show that the intrasellar lesion was accessed by the endoscopic endonasal biopsy (D, E). |
Hydrocortisone, 20 mg per day, was administrated soon after hypopituitarism was diagnosed in the patient. DI manifested after hydrocortisone replacement therapy. Desmopressin was taken as a nasal spray to control the central DI. An endoscopic transnasal biopsy was performed (Fig. 3). Sufficient specimens to diagnose were obtained without morbidities including cerebrospinal fluid leakage. Pathological examination showed a biphasic population of mature lymphocytes and larger germinoma cells compatible with pure germinoma (Fig. 3). Serial MR imaging showed regression of the suprasellar lesion after cranial computed tomography (CT) during radiation therapy planning (Fig. 4). The patient was treated with craniospinal irradiation. MR imaging demonstrated that the intracranial lesions (Fig. 5, 6) and the spinal lesion (Fig. 2A, B) disappeared after completion of radiation therapy (Fig. 2C, D). The serum level of beta-hCG and CSF levels of beta-hCG and PLAP were normalized (Table 2) after completion of craniospinal irradiation. The patient obtained remission and regained a nearly normal level of activity under hormone replacement therapy including hydrocortisone, levothyroxine and desmopressin. Restriction of her visual fields, however, did not improve sufficiently (Fig. 7). She returned to college after a 3-month absence. Goldmann perimeter revealed slight recovery of the left eye’s visual field 7 months after completion of radiation (Fig. 7).
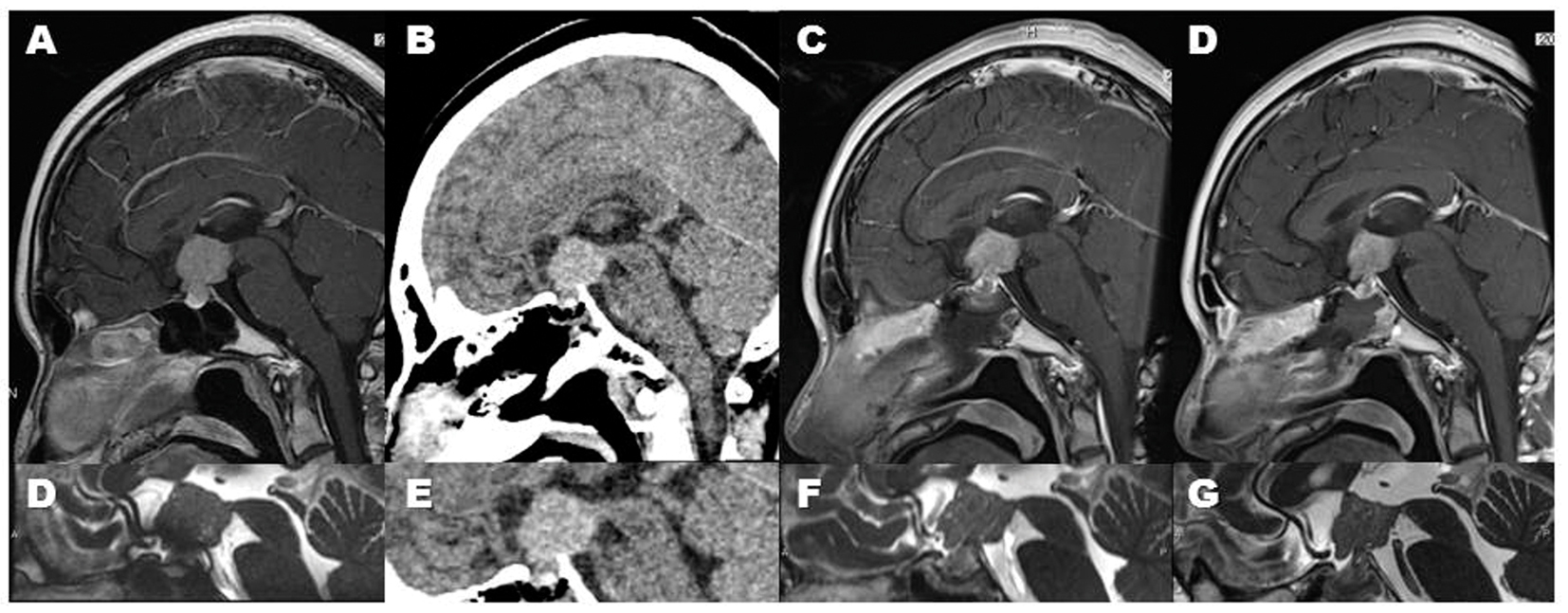 Click for large image | Figure 3. Serial images clearly demonstrated a regression of germinoma in this case. The regression was observed after the post-operative cranial computed tomography (CT) scan (B, E). Since this tumor is pure germinoma, this regression is compatible with diagnostic radiation-induced regression (DRIR). Sagittal MR images show the DRIR clearly: The tumor shows rapidly shrinking from the pre-CT-scanned state (A, D) through the third post-CT-scan day (C, F), to the eighth day (D, G). |
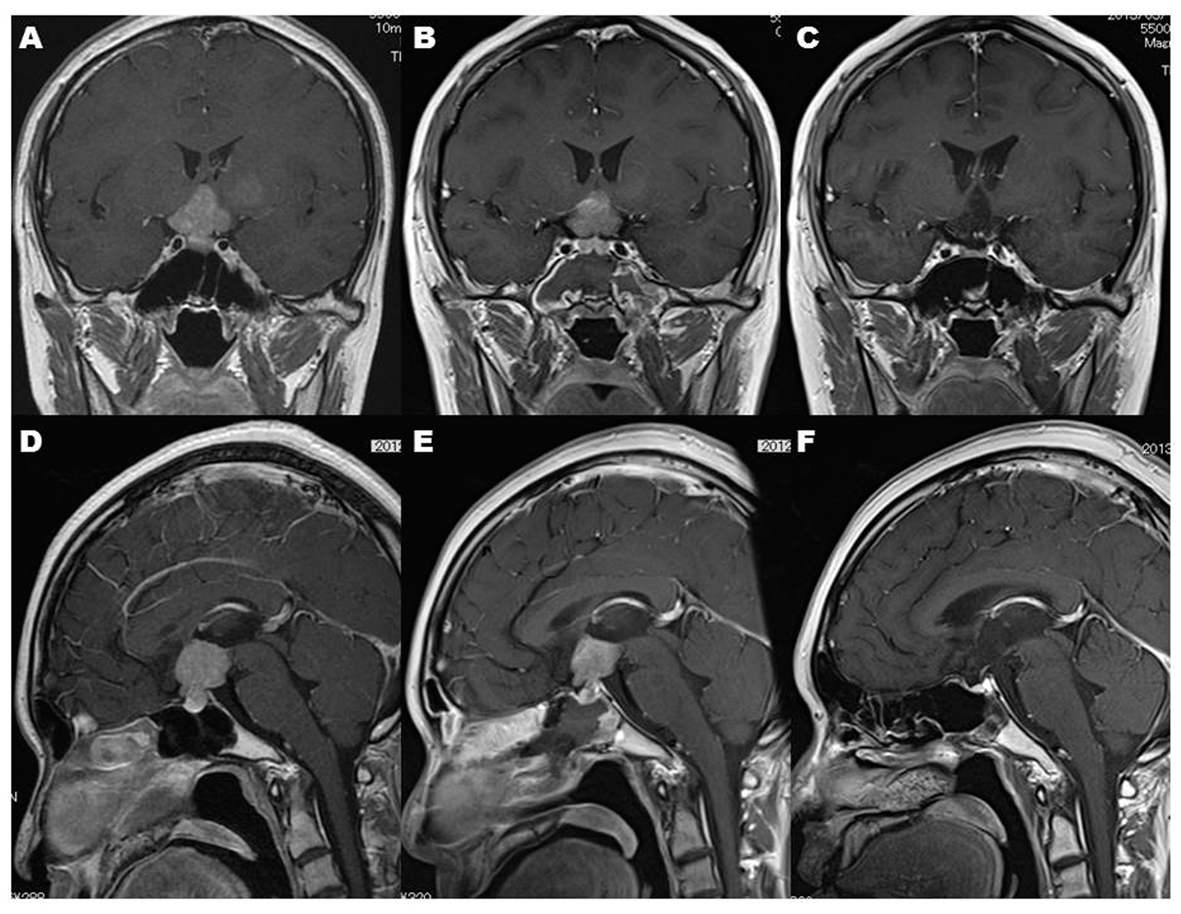 Click for large image | Figure 4. MR imaging demonstrates that the intracranial lesions before endonasal biopsy (A, D) and after endonasal biopsy (B, E) disappeared after completion of radiation therapy (C, F). Note that DRIR blurred the lesion of the left basal ganglia (A) after single cranial CT scan before radiation therapy (B). |
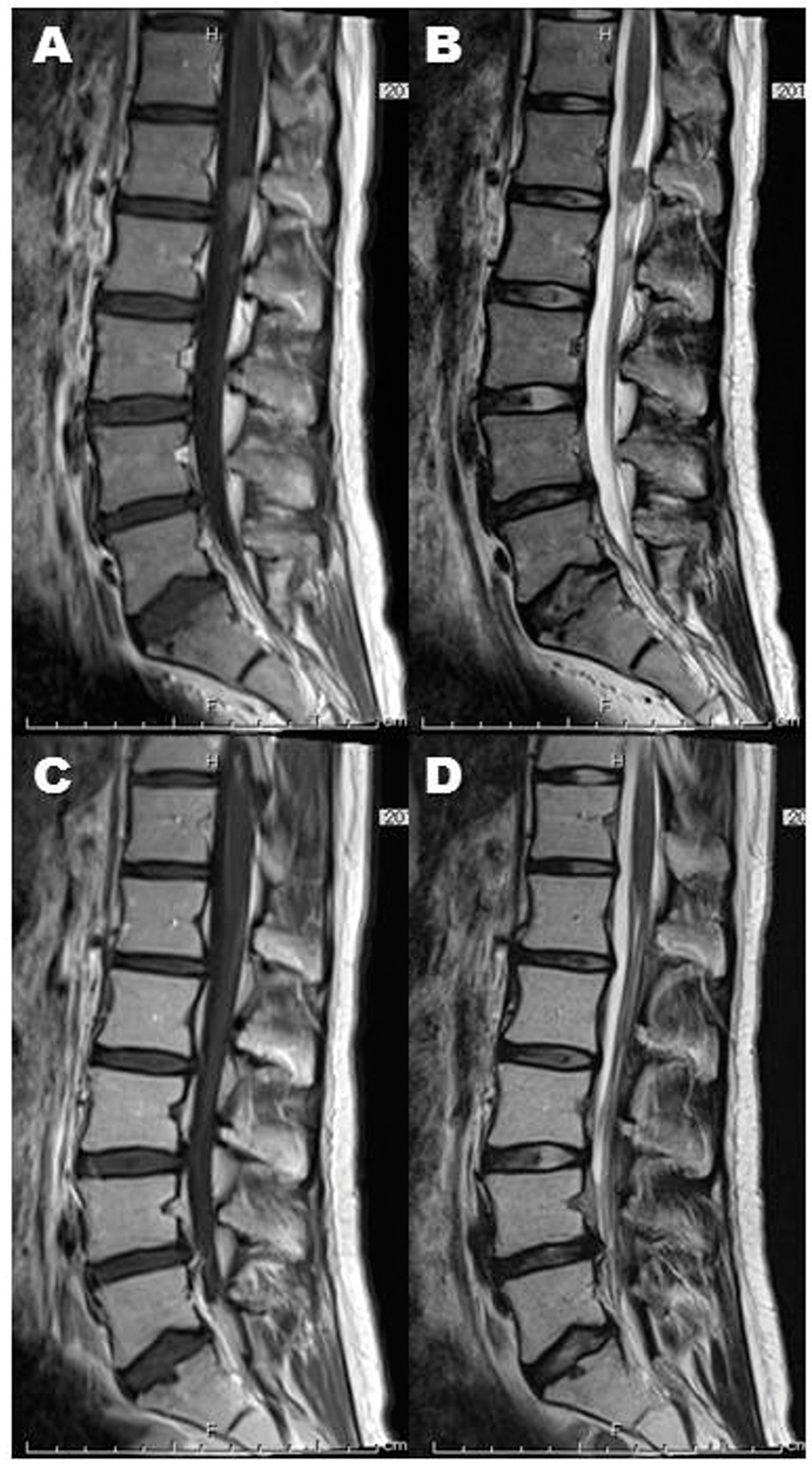 Click for large image | Figure 5. Spinal dissemination (A: post-contrasted sagittal image, B: T2-weighted sagittal image) also achieved complete remission (C: post-contrasted sagittal image, D: T2-weighted sagittal image). |
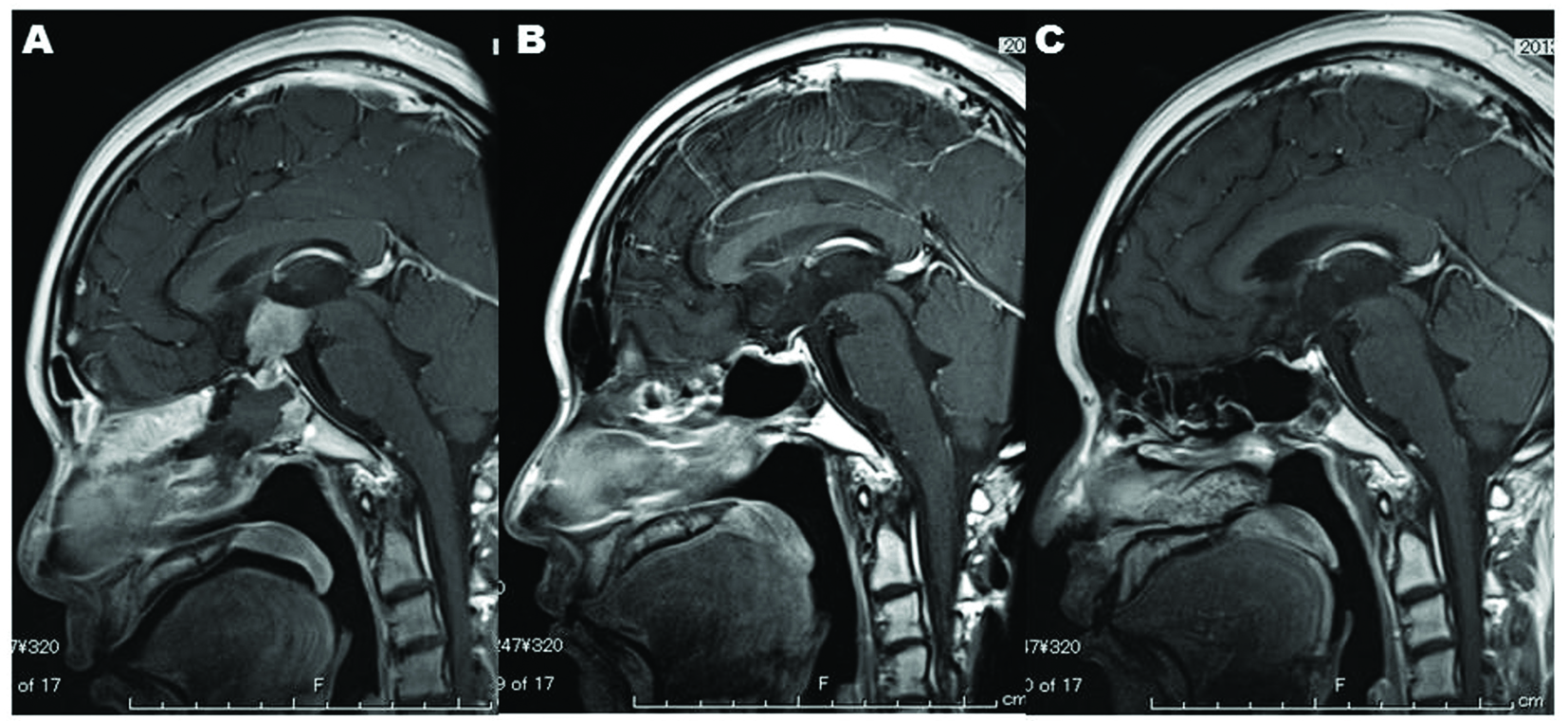 Click for large image | Figure 6. Nine months after completion of radiation, MR imaging shows no recurrence of the sellar-suprasellar lesion (C) and recovery of the intranasal and intrasphenoidal environments (C), which indicates that endoscopic endonasal biopsy is satisfactorily less-invasive. |
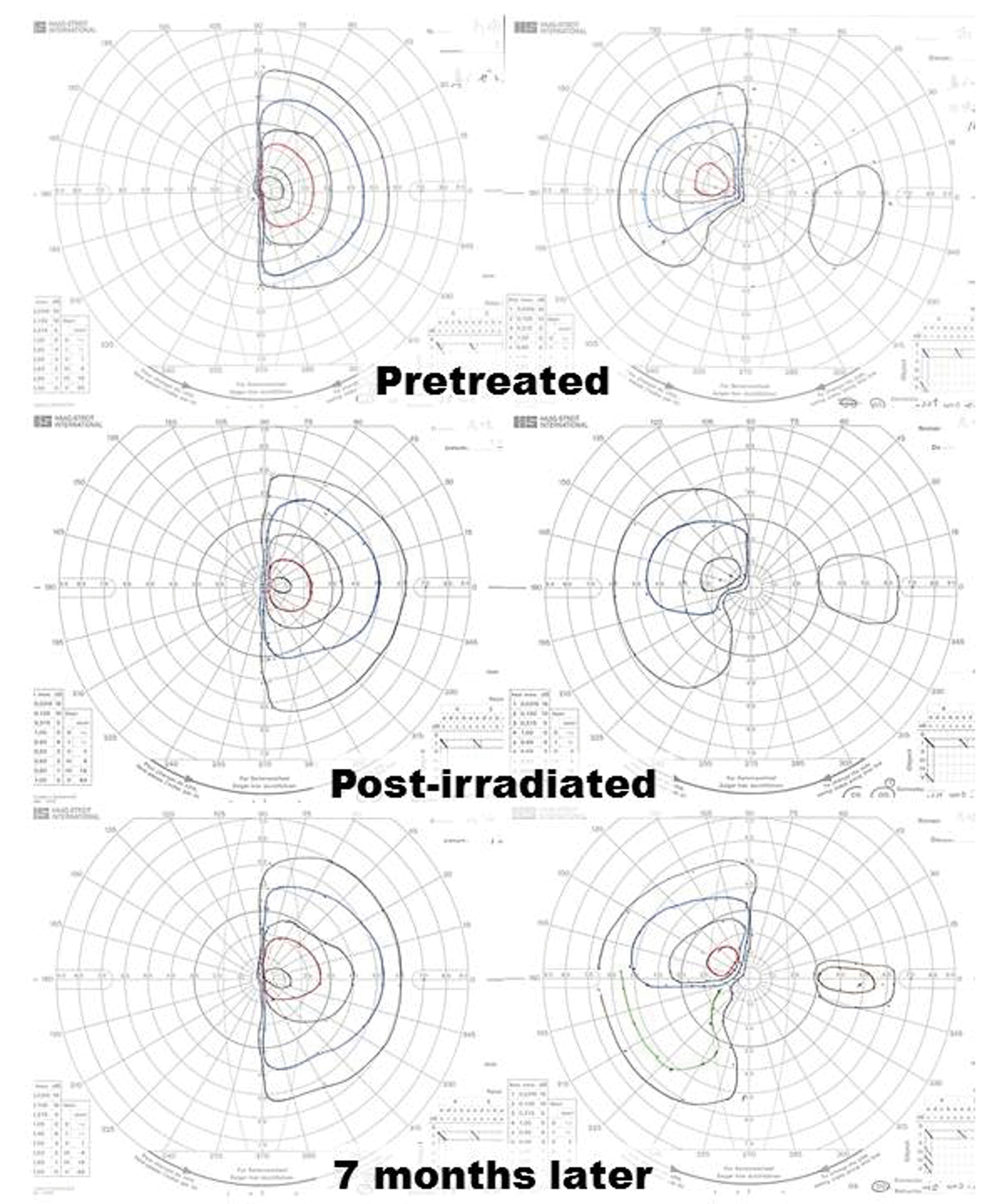 Click for large image | Figure 7. Despite complete remission of the lesion, restriction of the patient’s visual fields did not improve sufficiently. Goldmann perimeter revealed slight recovery of the left eye’s visual field 7 months after completion of radiation. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
After Ide et al reported the first suspected case of the regression of a primary intracranial germinoma [2], several reports about the regression of primary intracranial germinomas were added to the literature [3-6] as spontaneously regressed cases. We previously reported a case of synchronized multiple regression of primary intracranial germinoma [7] and concluded that the synchronized multiple regression did not occur spontaneously but was caused by diagnostic radiation. In other words, diagnostic radiation can cause a regression of germinoma.
In this report, we present serial MR images showing a regression of suprasellar germinoma after cranial CT scan. These findings of serial MR images advocate the existence of DRIR of germinoma. Here, we propose DRIR of germinoma as a new clinical entity.
Germinomas are so radiosensitive that they occasionally show regression after exposure to the radiation for diagnostic angiography [8]. This DRIR leads us to question whether previously reported spontaneous regressions of germinomas [2-6] are really “spontaneous” or not, because the patients in all of these cases were exposed to diagnostic radiation before regression, for example, plain X-ray films [3], CT scan(s) [2, 4-6] and angiography [3].
Si et al reported the case of a patient with a central nervous system germinoma that showed a significant regression in size following surgery and the administration of dexamethasone, prior to the initiation of chemotheraphy or therapeutic irradiation [9]. This patient, however, underwent multiple cranial CT scans. We speculated, even in this case, that DRIR is compatible with a cause of the regression of germinoma rather than the administration of dexamethasone.
Inadvertent diagnostic radiation can hide fine lesions to be treated, such as the lesion at the basal ganglia in our case (Fig. 1, 5A, 5B).
Regressions induced by diagnostic radiation may also indicate the high radiosensitivity of the lesion, which is a key to an accurate diagnosis of germinoma [7]. This provides a diagnostic and/or therapeutic clue and can help avoid radical resection [7].
Conclusion
Clinicians, particularly among the neurological fields, should keep this DRIR of germinoma in mind and should eliminate unnecessary irradiation to germinoma throughout the diagnostic process.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Doctor Shinichiro Watanabe, one of our seniors, for his help of PLAP measurement.
| References | ▴Top |
- Cole WH, Everson TC. Spontaneous regression of cancer: preliminary report. Ann Surg. 1956;144(3):366-383.
doi - Ide M, Jimbo M, Yamamoto M, Hagiwara S, Aiba M, Kubo O. Spontaneous regression of primary intracranial germinoma. A case report. Cancer. 1997;79(3):558-563.
doi - Fujimaki T, Mishima K, Asai A, Suzuki I, Kirino T. Spontaneous regression of a residual pineal tumor after resection of a cerebellar vermian germinoma. J Neurooncol. 1999;41(1):65-70.
doi pubmed - Murai Y, Kobayashi S, Mizunari T, Ohaki Y, Adachi K, Teramoto A. Spontaneous regression of a germinoma in the pineal body after placement of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt. J Neurosurg. 2000;93(5):884-886.
doi pubmed - Sato A, Sakurada K, Kuge A, Ito M, Akasaka M, Kayama T. [Spontaneous regression of primary intracranial germinoma: a case report]. No Shinkei Geka. 2009;37(3):277-282.
pubmed - Ono H, Shin M, Takai K, Oya S, Mukasa A, Saito N. Spontaneous regression of germinoma in the pineal region before endoscopic surgery: a pitfall of modern strategy for pineal germ cell tumors. J Neurooncol. 2011;103(3):755-758.
doi pubmed - Yoneoka Y, Tsumanuma I, Jinguji S, Natsumeda M, Fujii Y. Synchronized multiple regression of diagnostic radiation-induced rather than spontaneous: disseminated primary intracranial germinoma in a woman: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2011;5:39.
doi pubmed - Sawamura Y, de Tribolet N. Tumors of the pineal region. In Neuro-oncology of CNS tumors. Edited by: Tonn JC, Westphal M, Rutka JT, Grossman SA. Springer Science and Business; 2006:207-215.
doi - Si SJ, Khatua S, Dhall G, Nelson MD, Gonzalez-Gomez I, Finlay JL. Regression of primary central nervous system germinoma after dexamethasone administration: a case report. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2010;27(3):237-243.
doi pubmed
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Neurology Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.







