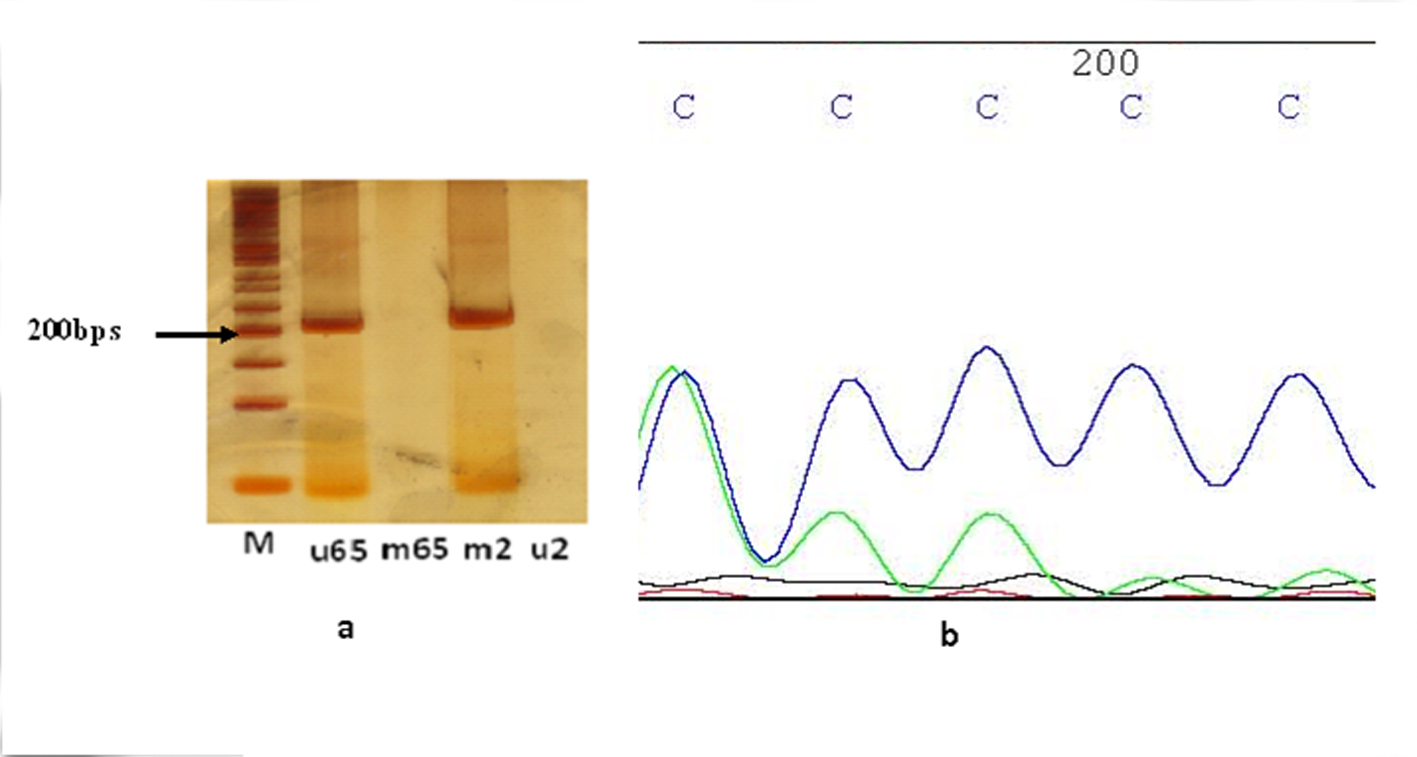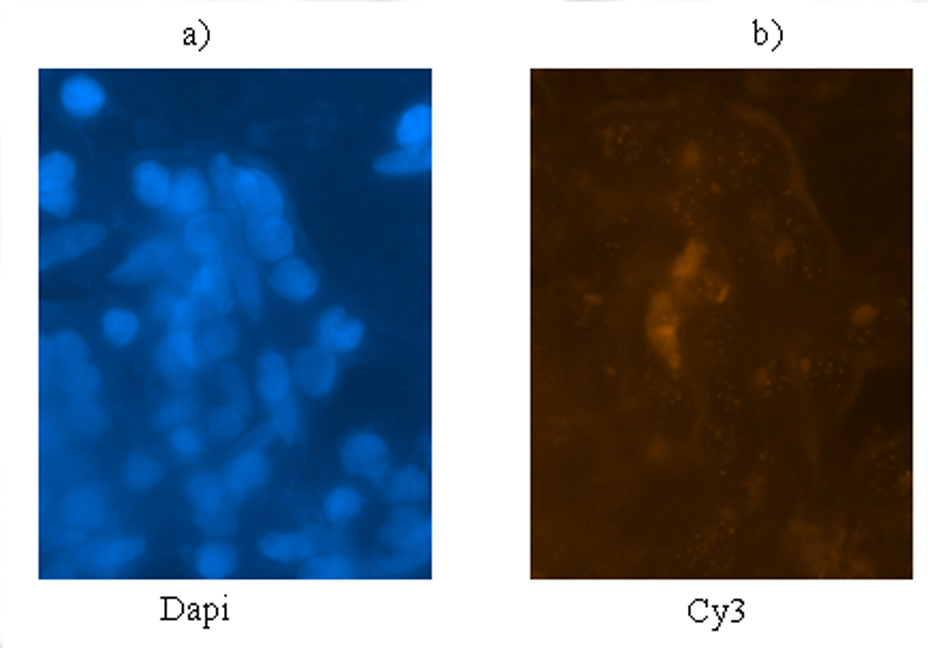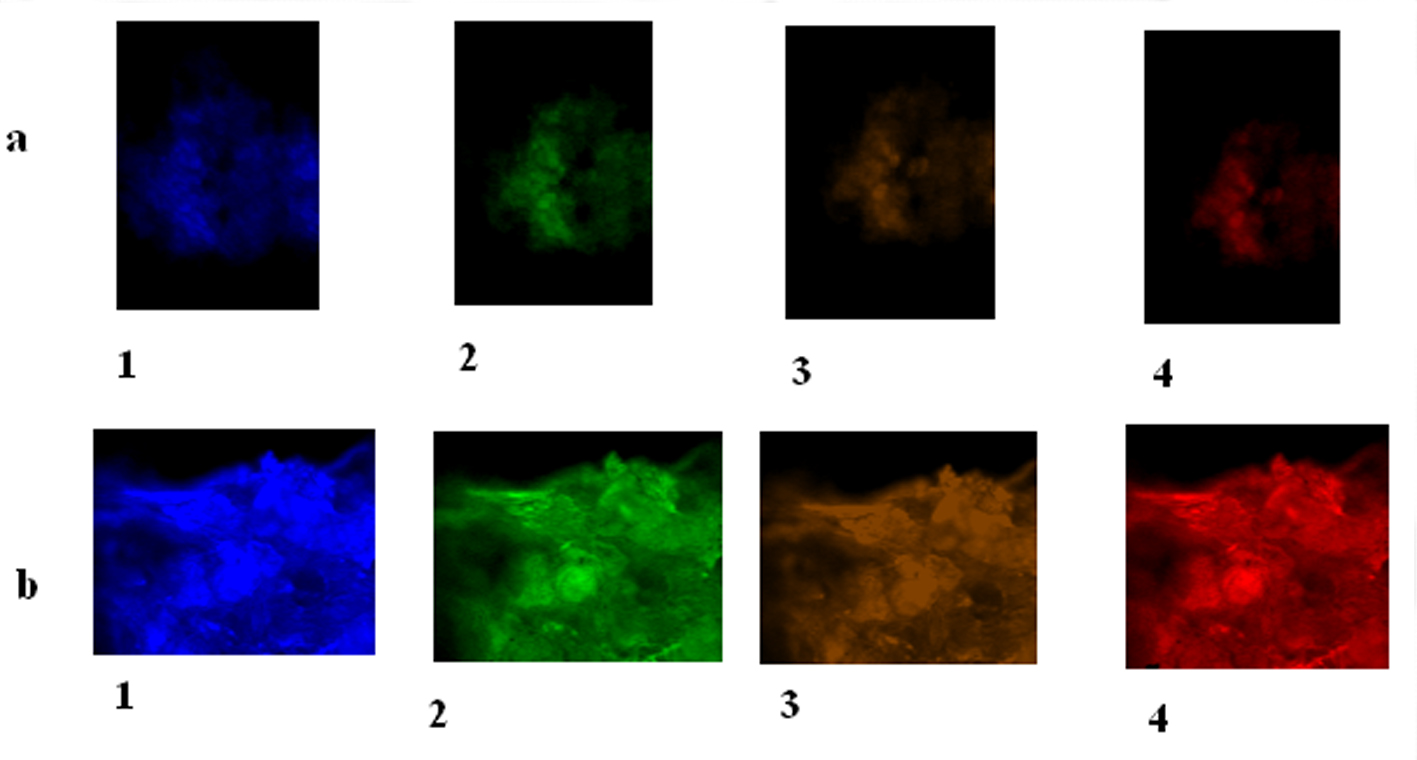
Figure 2. MCPH1 protein expression of cyclin E, CDC25A and MPCH1 in astrocytoma and meningioma tumors. (a) Brain tumor cells (BTCs) with astrocytoma. 1: BTC with DAPI filter; 2: BTC conjugated with FITC presenting low expression of cyclin E; 3: BTC conjugated with R-PE presenting low expression of CDC25A; 4: BTC conjugated with PE-Cy5 reflecting low expression of MCPH1 (× 100). (b) BTCs with meningioma. 1: BTC with DAPI filter; 2: BTC conjugated with FITC presenting high expression of cyclin E; 3: BTC conjugated with R-PE presenting low expression of cyclin E in majority of cells accompanied by clone of cells with high expression; 4: BTC conjugated with PE-Cy5 reflecting high expression of MCPH1 (× 100).