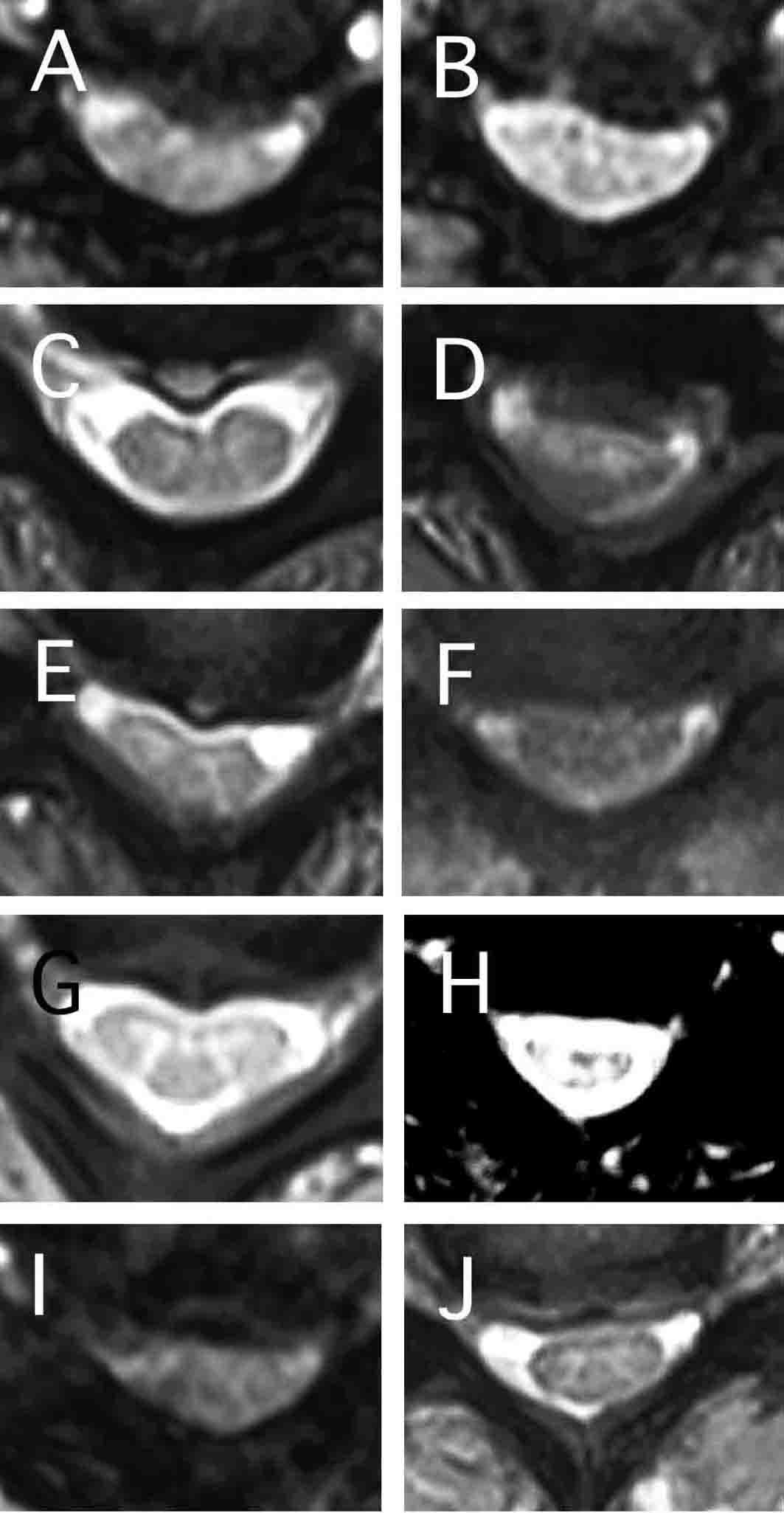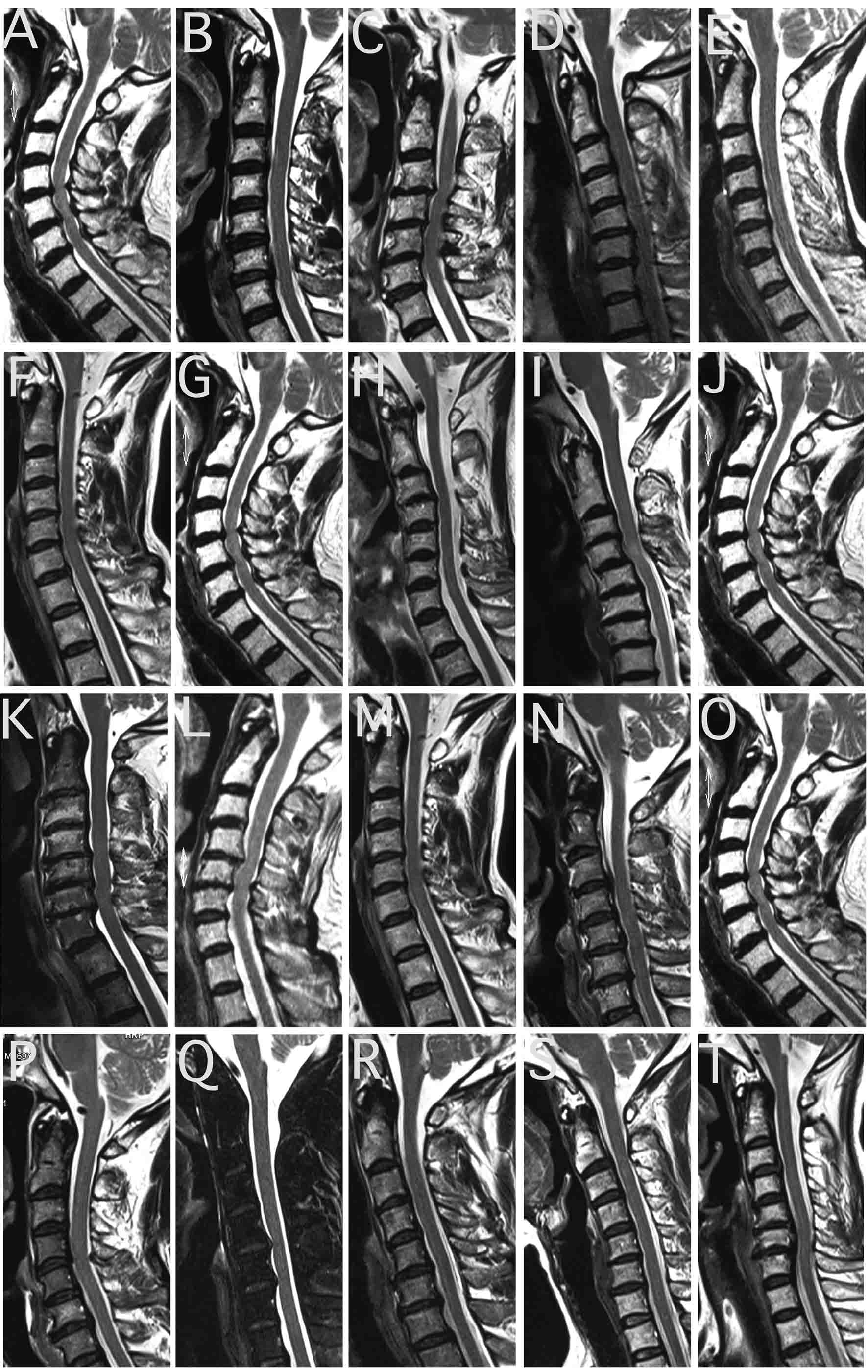
Figure 1. Sagittal T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (TR 500 TE 24). (A) Spinal cord compressions owing to C4-5, C5-6 intervertebral disk hernias were observed in Patient 1. (B) Spinal cord compressions owing to C6-7 (and mild C3-4) intervertebral disk hernias were observed in Patient 2. C3 vertebral level spinal cord showed a mild high intensity area and myelomalacia was suspected. (C) C3 vertebra was sliding posterior. C3-4, C4-5 (and mild C5-6) intervertebral level spinal cord compressions and spinal canal stenosis were observed in Patent 3. (D) Spinal cord compression owing to C5-6 intervertebral disk bulging and spinal canal stenosis were observed in Patient 4. (E) Spinal cord compression owing to C5-6 intervertebral level lesion was observed in Patient 5. (F) Spinal cord compression owing to C4-5 intervertebral disk hernia was observed in Patient 6. (G) Spinal cord compressions owing to C4-5 and C5-6 intervertebral disk bulging with osteophyte formations were observed in Patient 7. (H) Spinal cord compression owing to C3-4 intervertebral kyphosis deformity was observed in Patient 8. (I) Spinal cord compression owing to C4-5 intervertebral level lesion and a T2 high intensity area in C4 vertebral level spinal cord were observed in Patient 9. (J) Spinal cord compressions and deformity owing to C5-6 (and mild C4-5) intervertebral level lesions were observed in Patient 10. (K) Severe spinal cord compressions owing to C6-7 (mild C4-5 and C5-6) intervertebral disk bulging and osteophyte formations were observed in Patient 11. (L) Spinal cord compressions owing to C4-5 (and mild C5-6) intervertebral level lesions were observed in Patient 13. (M) Spinal cord compression owing to C4-5 intervetebral disk hernia was observed in Patient 17. (N) Spinal cord compression and mild deformity owing to C5-6 intervertebral disk hernia and hypertrophy of the posterior longitudinal ligament lesion were observed in Patient 18. (O) Spinal cord compressions owing to C5-6 (mild C4-5 and C6-7) intervertebral disk bulging were observed in Patient 19. (P) Spinal cord compression owing to C4-5 intervertebral disk bulging was observed in Patient 20. (Q) Spinal cord compressions owing to C4-5 and C5-6 intervertebral level osteophyte formations were observed in Patient 21. (R) Right side dominant spinal cord compressions owing to C4-5 and C5-6 intervertebral disk hernias were observed in Patient 22. (S) Spinal cord compression owing to C5-6 intervertebral disk bulging was observed in Patient 23. (T) Spinal cord compression owing to osteophyte formation of C6 vertebra and hypertrophy of posterior longitudinal ligament was observed in Patient 24.