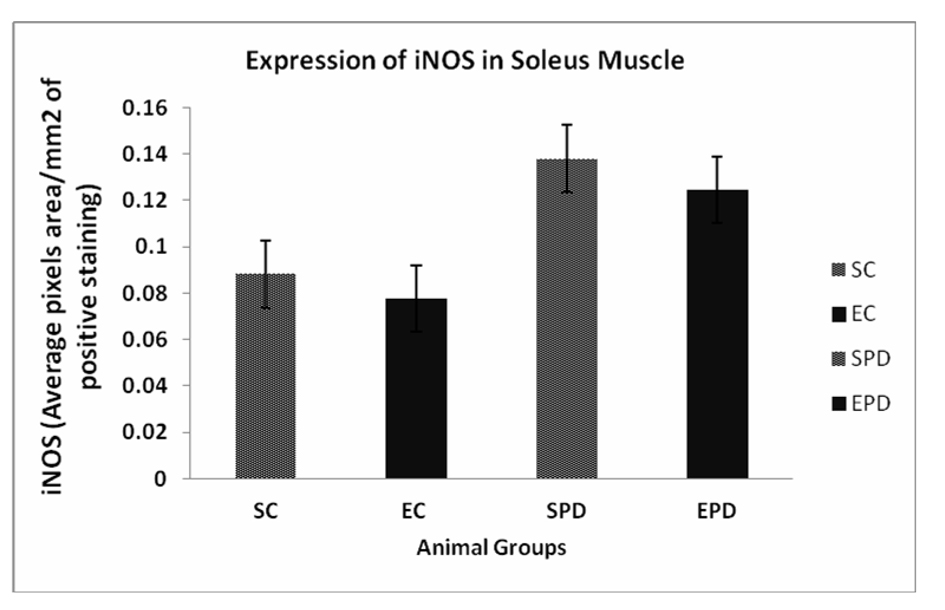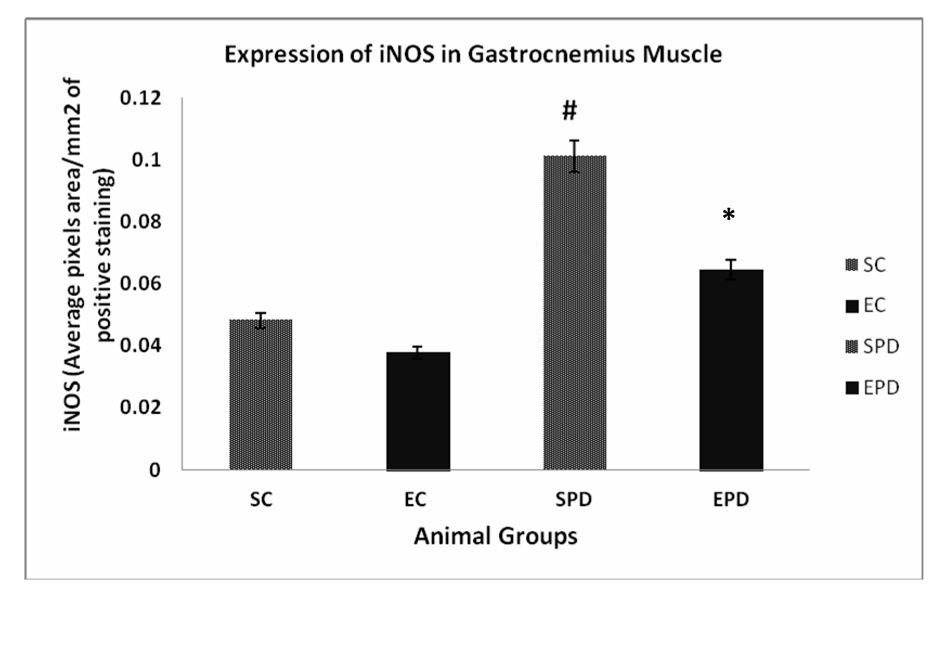
Figure 1. Expression of iNOS in gastrocnemius muscle showed significant increase in expression of iNOS is SPD group compared to SC, # P value < 0.05. Exercise did not significantly decrease the expression of iNOS in control group P value < 0.18. However, exercise significantly decreased iNOS expression in PD-induced group, * P value < 0.01. iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide sysnthase. SC: Sedentary control, EC: Exercised control, SPD: Sedentary Parkinson’s disease, EPD: Exercised Parkinson’s disease.