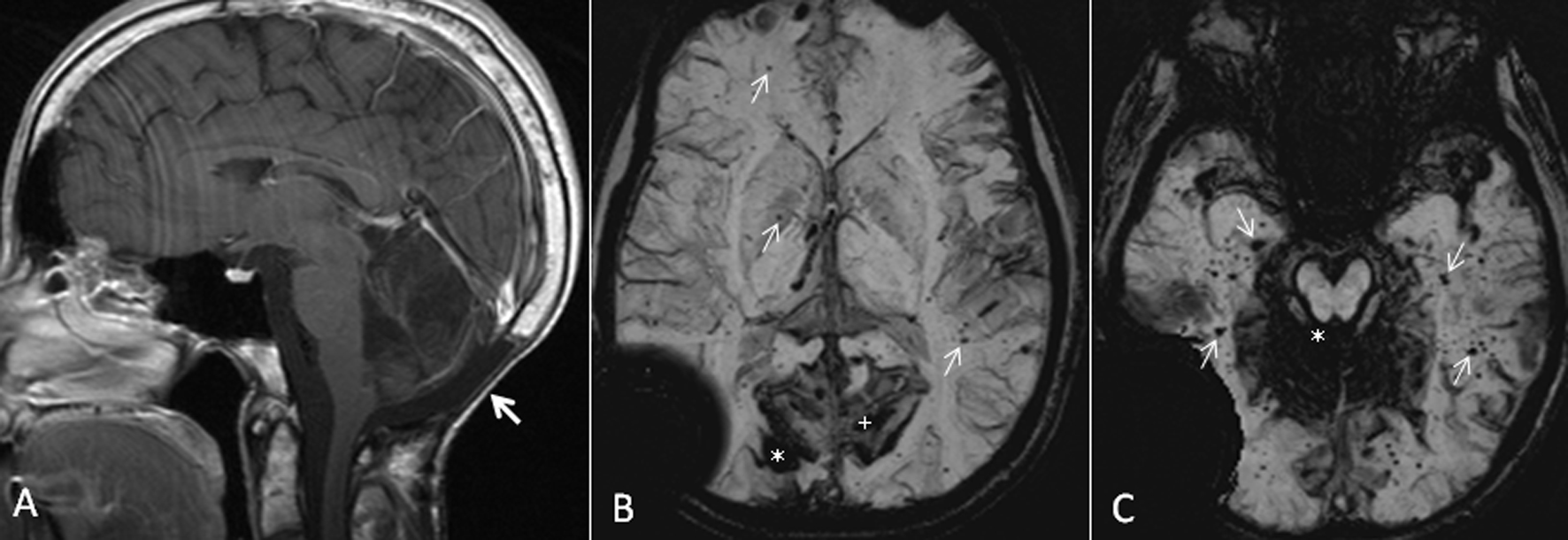
Figure 1. (A) Sagittal T1 post-gadolinium image demonstrates post-operative changes of suboccipital craniectomy and resection of medulloblastoma in the posterior fossa (arrow). (B) Axial susceptibility-weighted minimum intensity pixel (mIP) image demonstrates prominent signal drop from the right occipital cavernoma (*). Note the prominent susceptibility signals in the adjacent sulci in bilateral medial parieto-occipital regions from intense pial hemosiderin staining (+). Also, note the multiple tiny signal dropouts scattered throughout the brain from small cavernomas and telangiectasia, some of them marked with arrows. The large signal drop in the right temporopariteal region extending outside the calvarium is from the shunt reservoir. (C) Axial susceptibility-weighted mIP image demonstrates superficial siderosis causing signal drop in the cerebellar folia and the pial surface of brainstem (*). Also note numerous tiny signal dropouts in the bilateral temporal lobes and occipital lobes from radiation-induced cavernomas and telangiectasia (arrows).