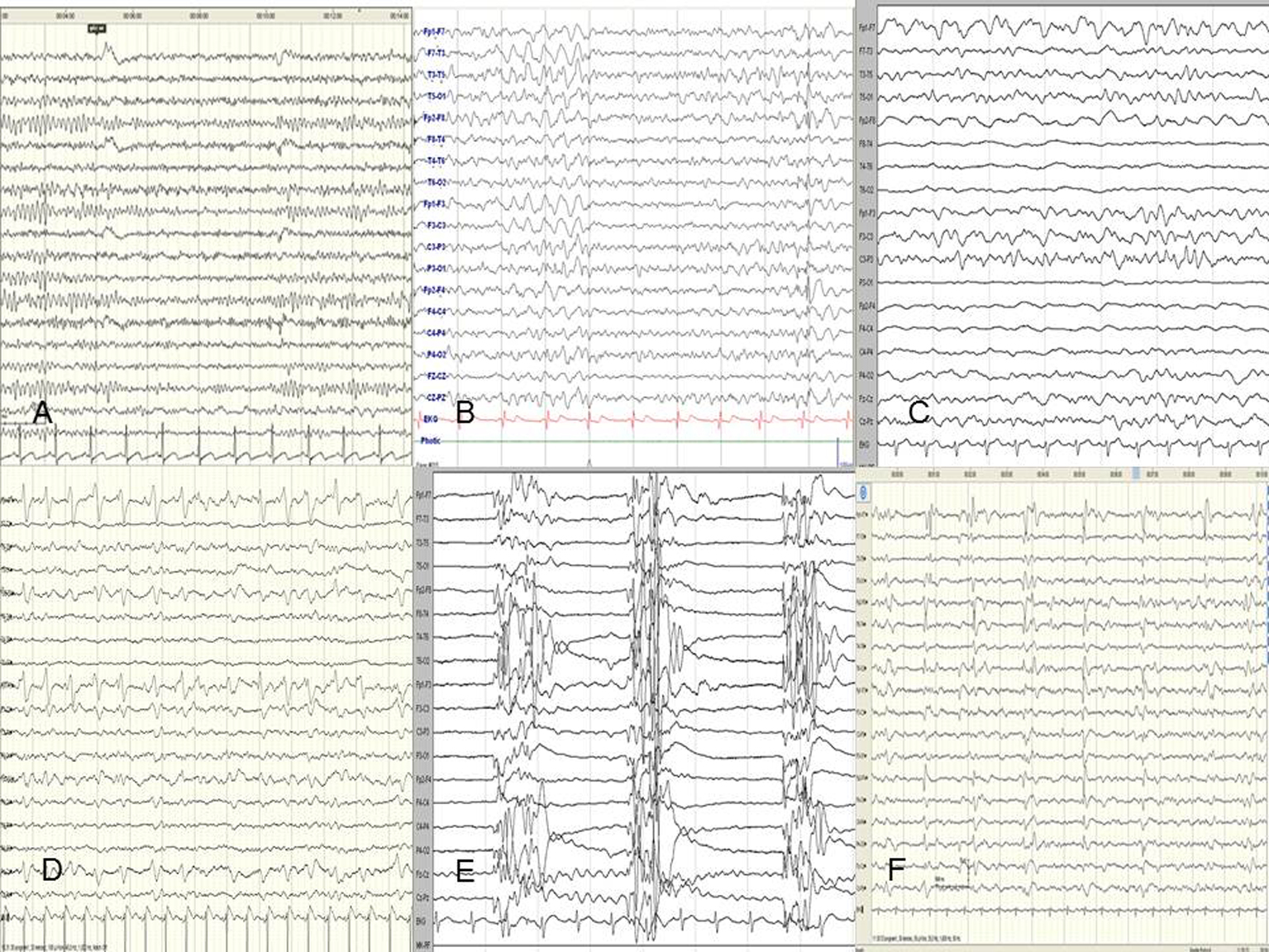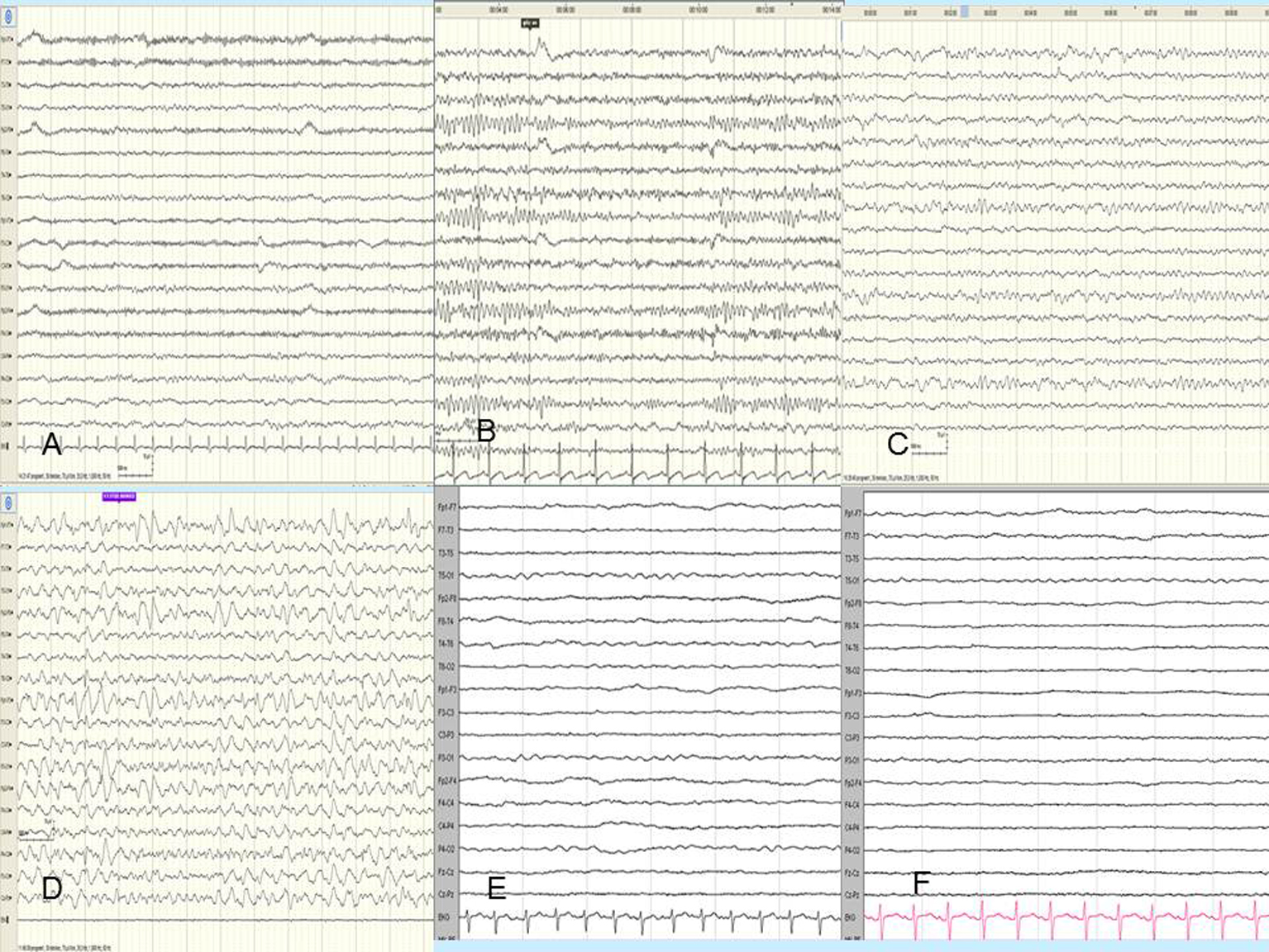
Figure 1. (A) Normal ground rhythm. (B) Decreased alpha activity that reacts to opening and closing of the eye and the recordings with partially increased tetha waves. (C) Recordings that show locally observed alpha activity that does not react to opening and closing of the eye, extensive tetha activity and sometimes brief paroxysms of concomitant delta activity. (D) Ground activity with extensive high-amplitude delta activity. (E) Ground rhythm with low-amplitude delta activity. (F) Isoelectric EEG recording.