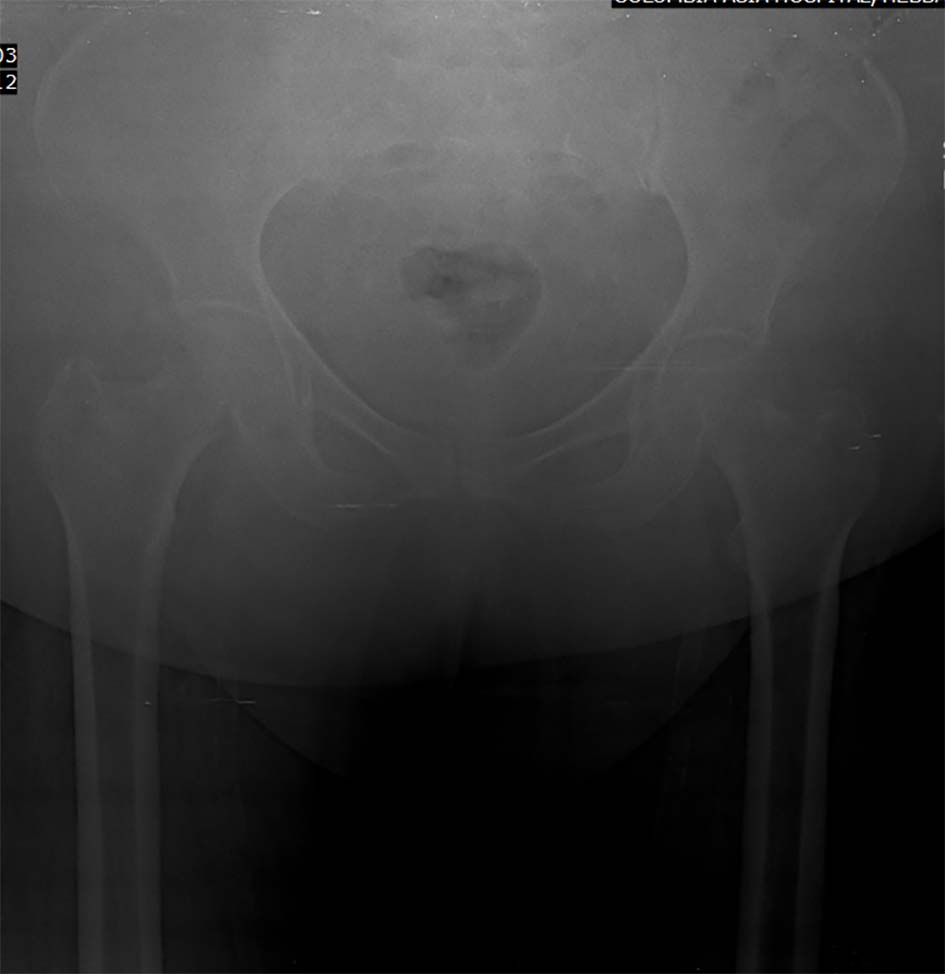
Figure 1. Fracture of right inferior pubic ramus.
| Journal of Neurology Research, ISSN 1923-2845 print, 1923-2853 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Neurol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.neurores.org |
Case Report
Volume 6, Number 5-6, December 2016, pages 114-117
Fat Embolism Syndrome: Case Report
Figures

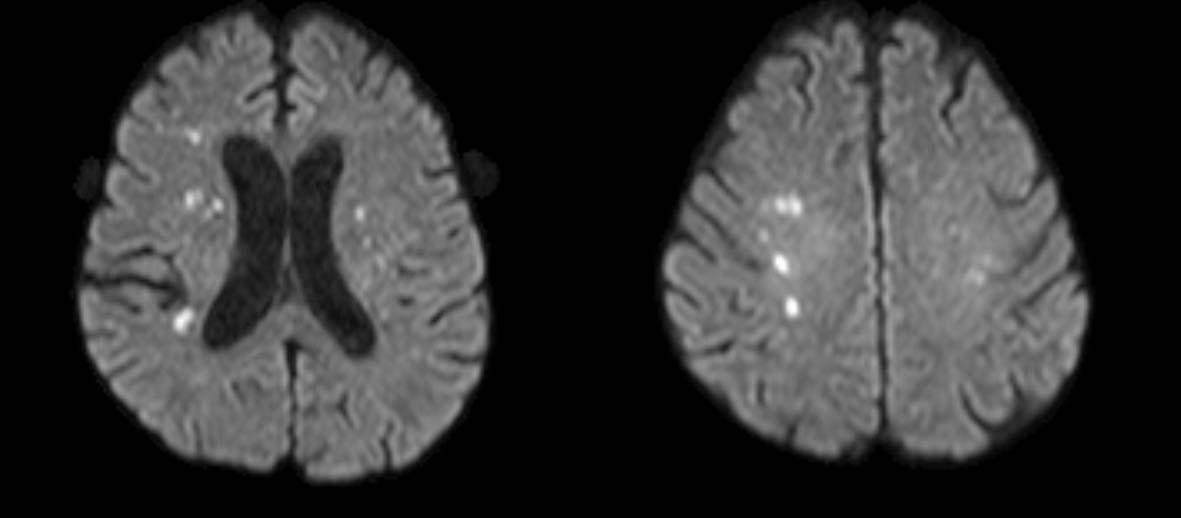
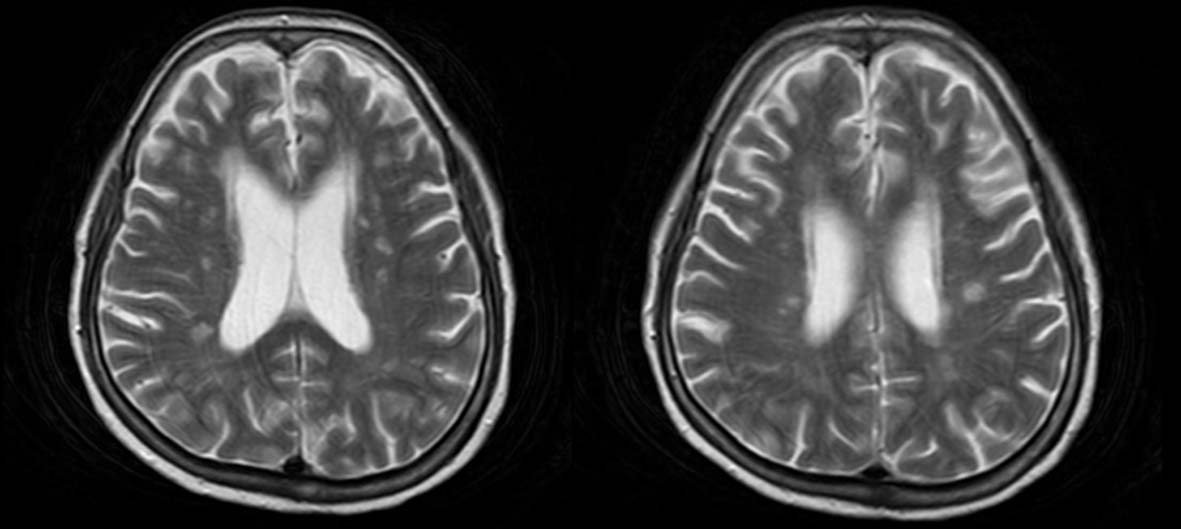
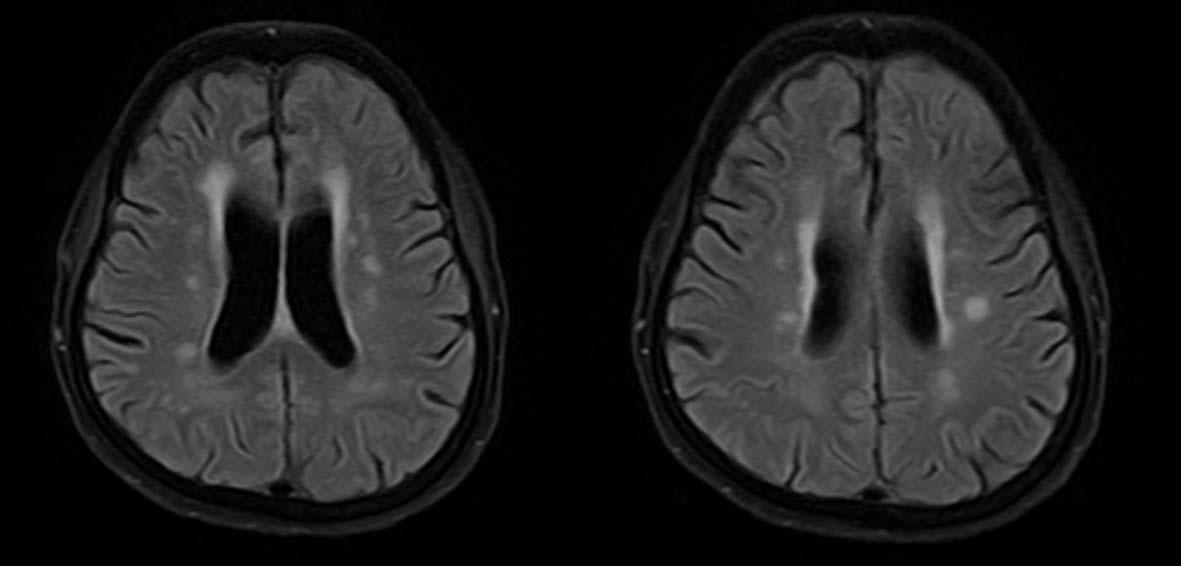
Tables
| Blunt trauma (approximately 90% of all cases) |
| Acute pancreatitis |
| Diabetes mellitus |
| Burns |
| Joint reconstruction |
| Cardiopulmonary bypass |
| Liposuction |
| Decompression sickness |
| Sickle cell crisis |
| Parenteral lipid infusion |
| Pathologic fractures |
| Major features | Minor features |
|---|---|
| ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate. | |
| Axillary or subconjunctival petechiae | Tachycardia > 110/min |
| Hypoxemia PaO2 < 60 mm Hg; FIO2 = 0.4 | Pyrexia > 38.5 |
| Pulmonary edema | Retinal fat or petechiae |
| Sudden drop in Hb level > 20% | Urinary fat globules or oligoanuria |
| Central nervous system depression disproportionate to hypoxemia | Sudden thrombocytopenia > 50% High ESR > 71 mm/h |
| Criteria | Score |
|---|---|
| Petechiae | 5 |
| X-ray chest diffuse infiltrates | 4 |
| Hypoxemia | 3 |
| Fever | 1 |
| Tachycardia | 1 |
| Confusion | 1 |
| 1. Sustained PO2 < 8 kPa |
| 2. Sustained PCO2 > 7.3 kPa |
| 3. Sustained respiratory rate > 35/min, in spite of sedation |
| 4. Increased work of breathing, dyspnea, tachycardia, anxiety |