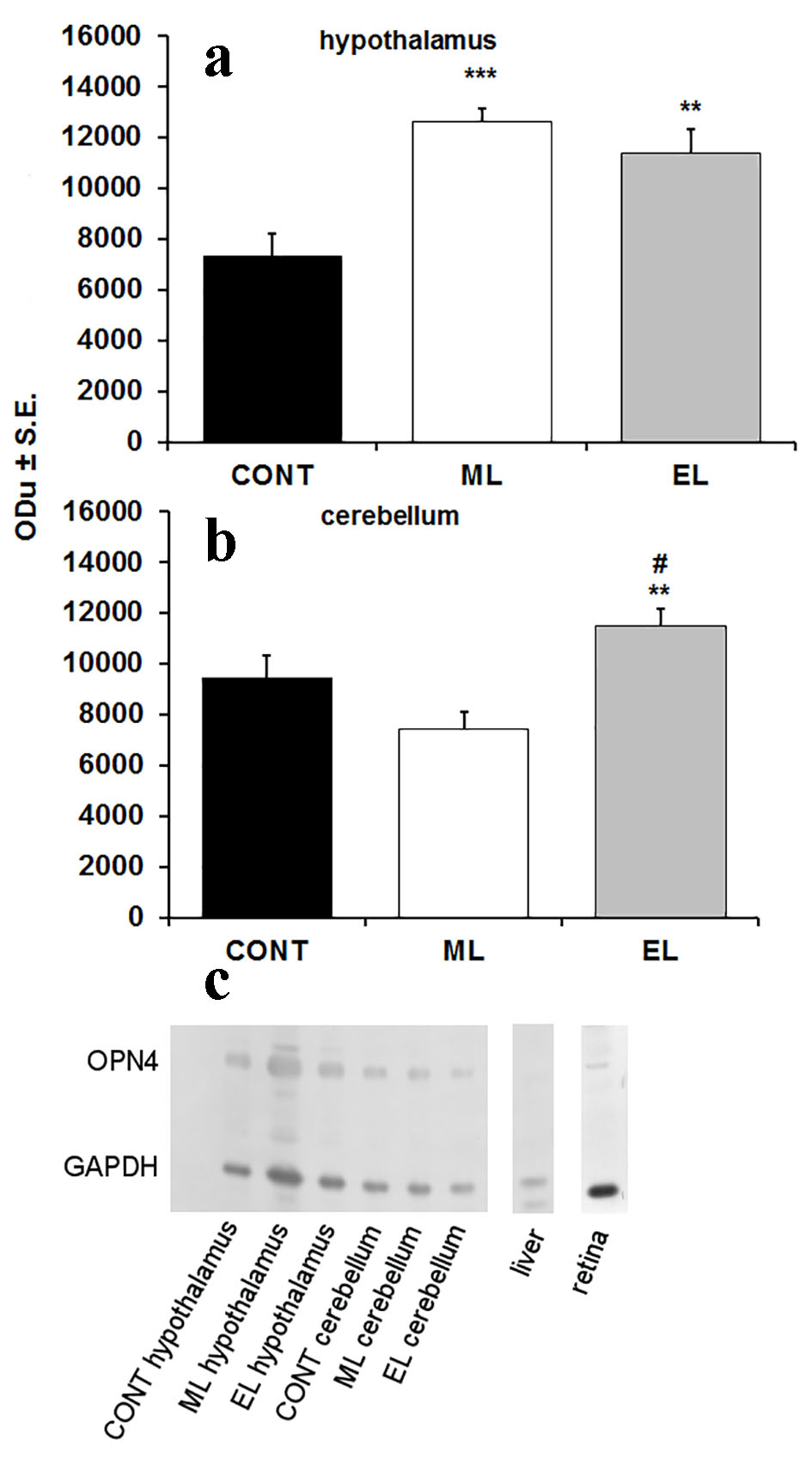
Figure 1. Expression of OPN4 in hypothalamus and cerebellum of mouse brain. (a) A bar graph summarizing results from Western blot analysis showing mean optical density (ODu) of OPN4 in relation to GAPDH in hypothalamus (N = 10 samples per group). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; error bars indicate SE. (b) A bar graph summarizing results from Western blot analysis showing mean optical density (ODu) of OPN4 in relation to GAPDH in cerebellum (N = 10 samples per group). **P < 0.01; error bars indicate SE. # marks the significance compared to ML group, ##P < 0.001. (c) A representative Western blot membrane showing expression of OPN4 with a molecular weight of 53 kDa. GAPDH was used as a loading control with a molecular weight of 37 kDa. CONT: control group; ML: morning-light group; EL: evening-light group.