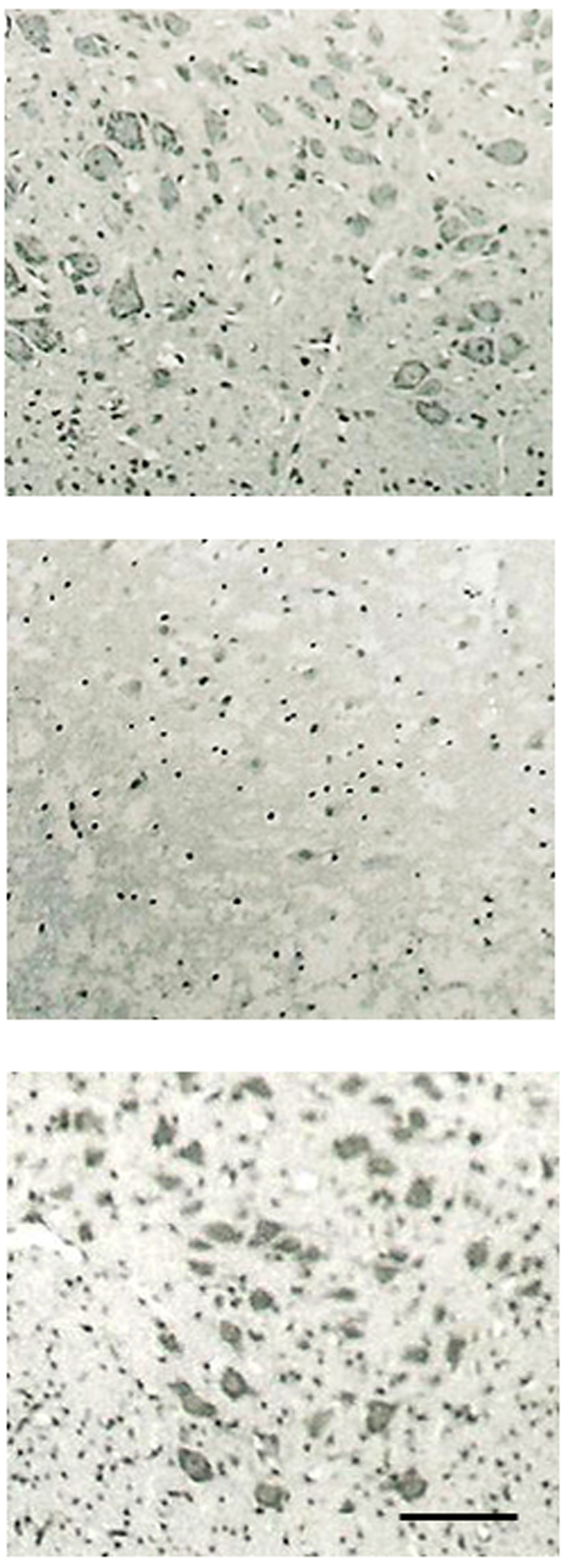

Figure 1. Morphology of spinal motor neurons. Effect of PPX on organotypic cultures of rat spinal cord. Upper: control cultures; Middle: glutamate-treated culture; Lower: co-treatment with glutamate and PPX-treated cultures. (The bar represents 50 µm); Treatment with glutamtate produced a marked loss of spinal motor neurons compare to control culture; Treatment with PPX protected spinal motor neuron loss against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity.
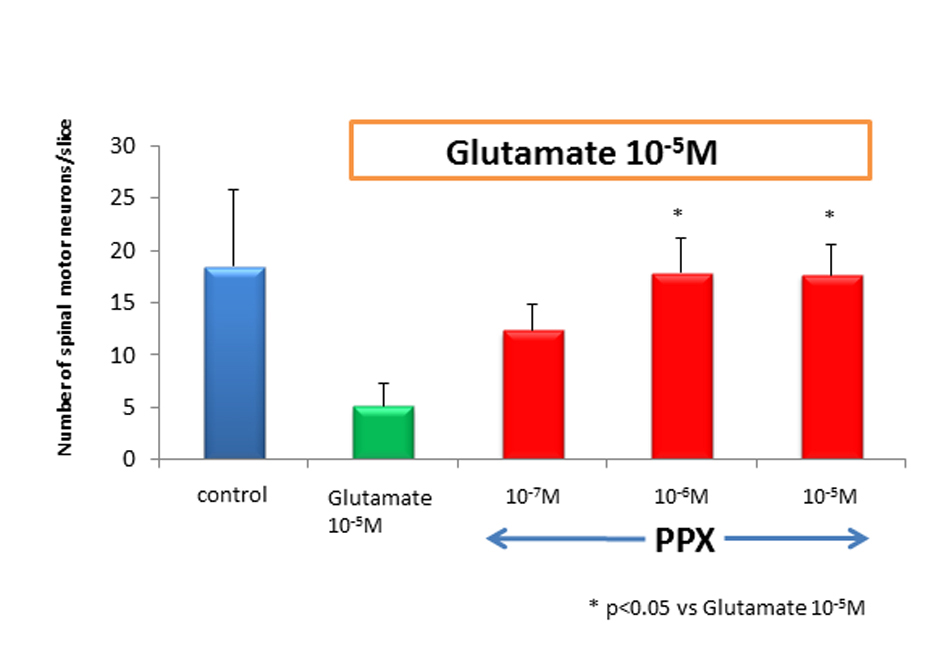
Figure 2. Number of spinal motor neurons. After 2 weeks of cultures, the number of spinal motor neurons in glutamate-treated cultures dropped by approximately 80% as compared to control. PPX act 10-6 M and 10-5 Mprotected spinal motor neurons against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity.
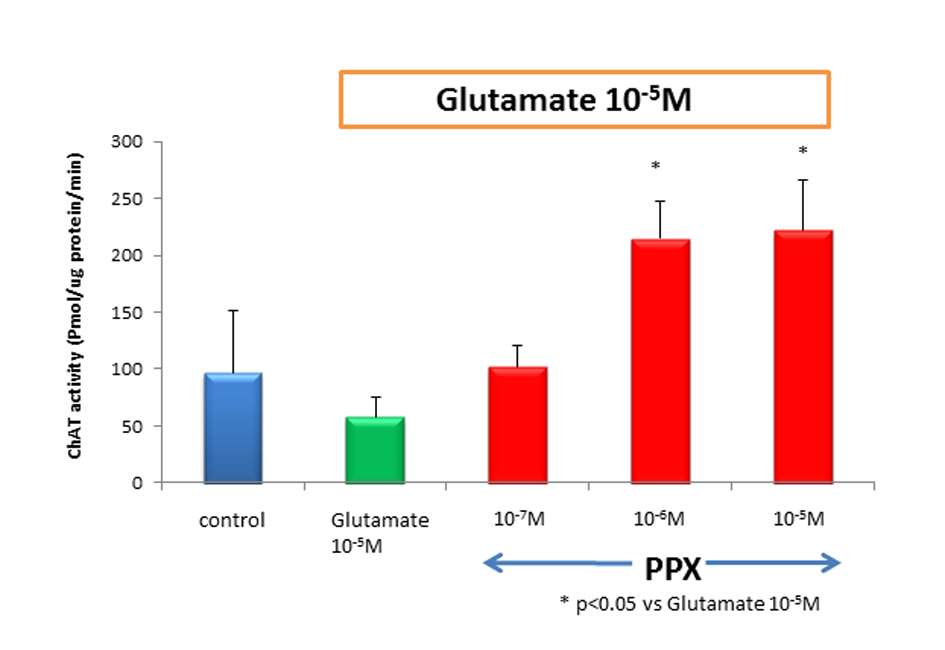
Figure 3. ChAT activity treatment of cultures with 10-5 Mglutamate reduced ChAT activity approximately to 40% of untreated control. However, cotreatment of 10-6 M of PPX and glutamate was significantly neuroprotective, compared with glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. Culture treatment was 2 weeks.


