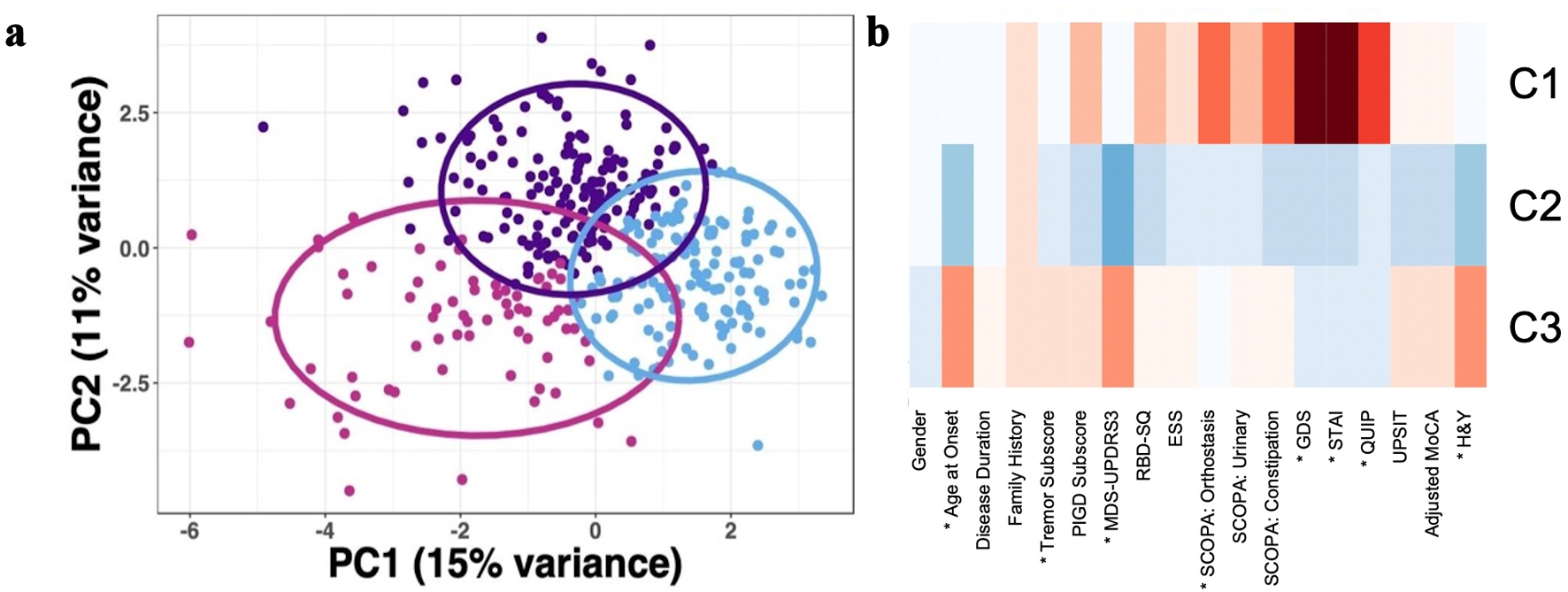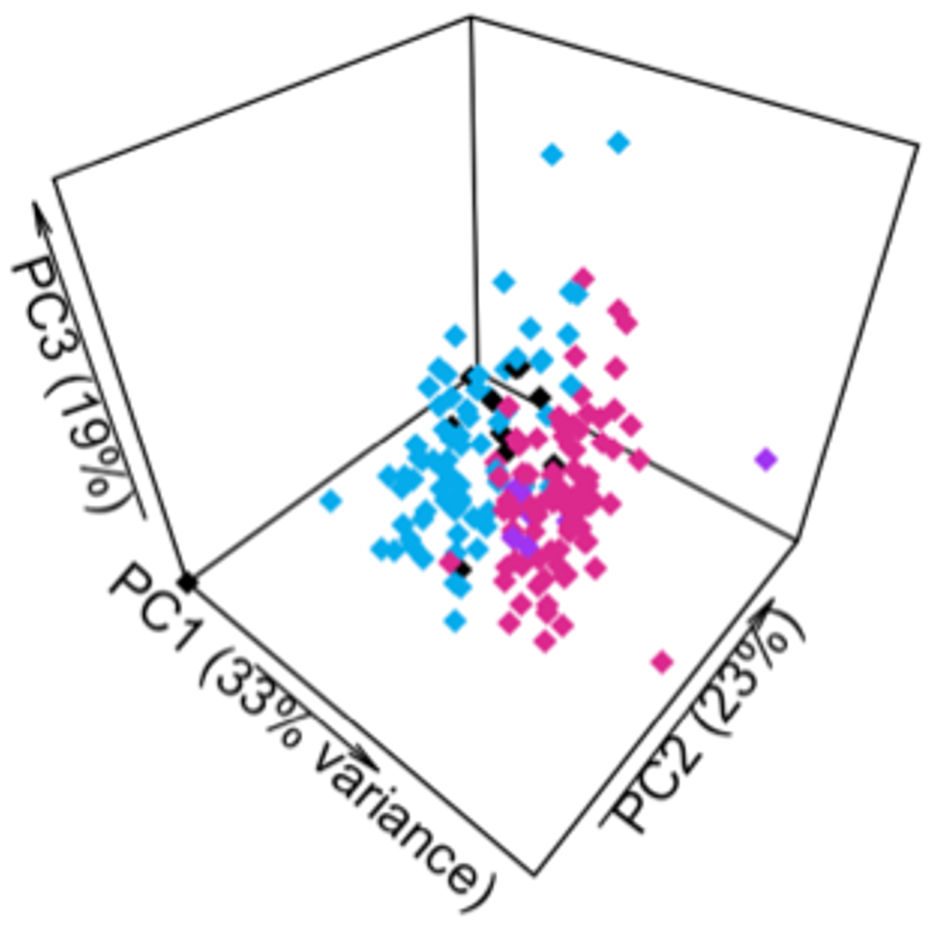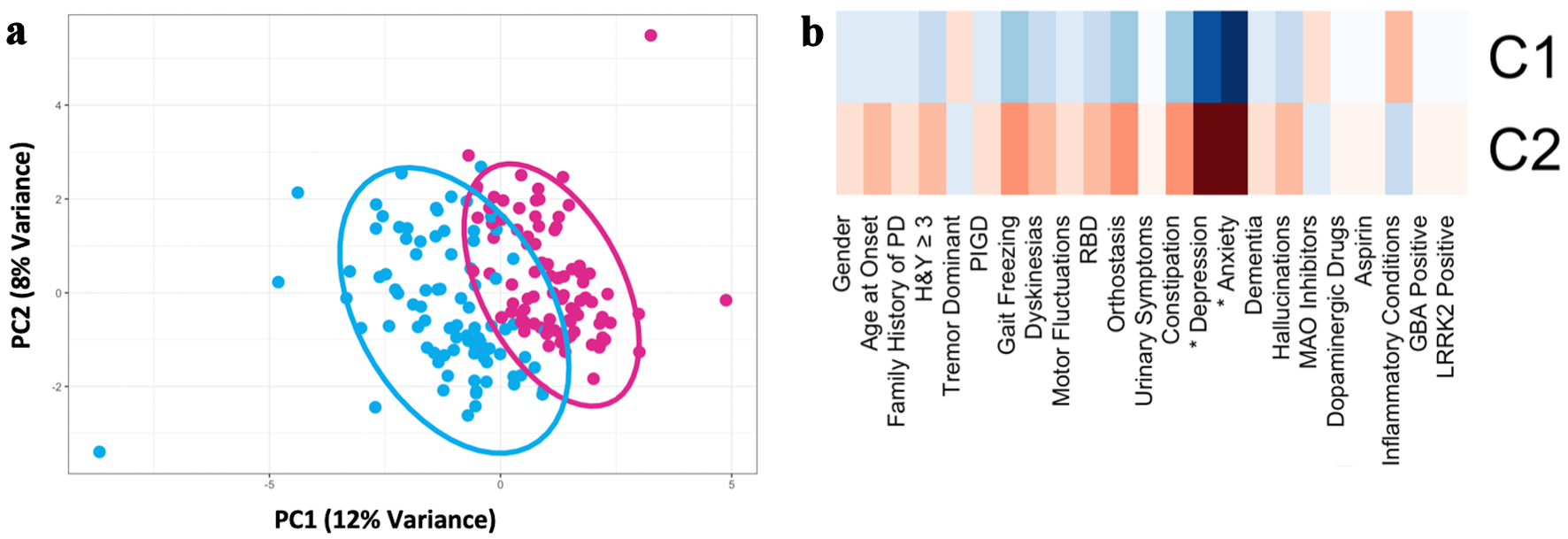
Figure 1. Principal component analysis of the discovery cohort (n = 179) based on demographic, motor, and nonmotor characteristics demonstrated two PD subtypes (after imputing missing data and controlling for disease duration). (a) Scatter plot depicting separation of subjects across the first two principal components. (b) Heatmap of clinical characteristics for each cluster identified. The greater red hue indicates greater prevalence, greater blue hue indicates lower prevalence. Traits with a statistically significant difference between clusters, defined as Bonferroni corrected P < 0.05, are indicated with an asterix (*). PD: Parkinson’s disease; RBD: REM-sleep behavior disorder; MAO: monoamine oxidase; PIGD: postural instability and gait disorder; GBA: glucocerebrosidase; LRRK2: leucine-rich repeat kinase 2; H&Y: Hoehn and Yahr scale; PC: principal component.