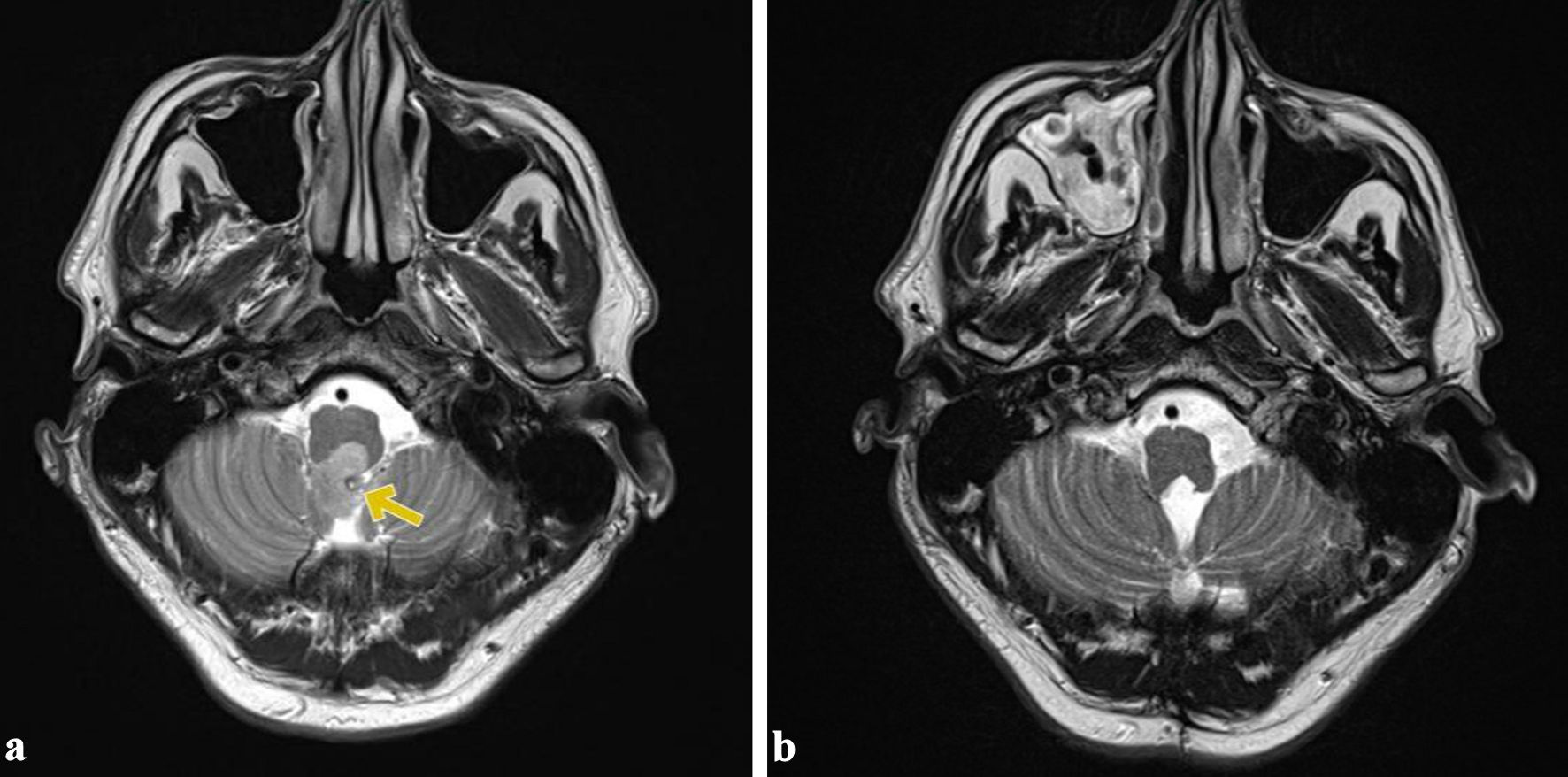
Figure 1. Preoperative and postoperative appearances. (a) The fourth ventricle lesion (yellow arrow). (b) Postoperative image showing total resection of the lesion.
| Journal of Neurology Research, ISSN 1923-2845 print, 1923-2853 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Neurol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.neurores.org |
Case Report
Volume 14, Number 2, September 2024, pages 86-89
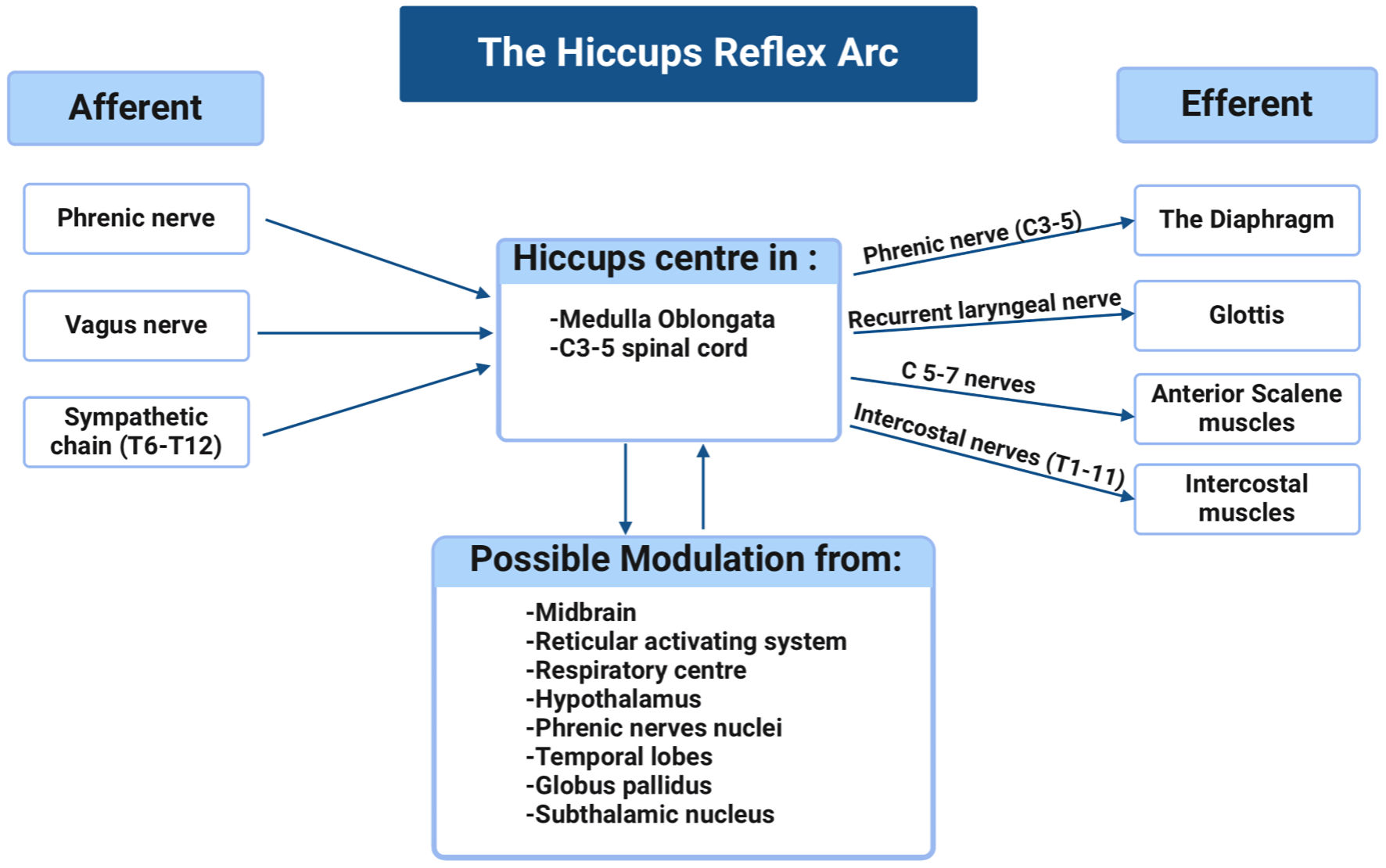
Vagal Nerve Stimulation for Intractable Hiccups
Figures

Table
| Case | Age (years) | Sex (M/F) | Hypothesized cause of hiccups | Procedure | Outcome | Side effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M: male; F: female; VNS: vagus nerve stimulation; SOL: space occupying lesion. | ||||||
| Payne et al, 2005 [12] | 51 | M | Three successive cerebellar strokes requiring decompressive craniectomy | VNS | Complete relief of hiccups | None |
| Grewal et al, 2018 [13] | 52 | M | Postoperative hiccups | VNS | No relieve | |
| Pierluigi et al, 2010 [14] | 69 | M | Left insular ischemic stroke | VNS | Partial | Stopped due to side effect |
| Schulz-Stubner et al, 2011 [15] | 47 | M | Severe left basal ganglia and intraventricular bleed with hydrocephalus | transcutaneous nerve stimulator | Complete | |
| Tariq et al, 2021 [16] | 85 | M | Post chest infection | VNS | Complete | |
| De Vloo et al, 2018 [17] | 59 | F | No obvious cause detected | VNS | Complete | |
| Our case | 64 | M | Post posterior fossa craniotomy for SOL | VNS | Complete | |